Dosing & Uses
Dosage Forms & Strengths
capsule, immediate-release (Prograf, Hecoria)
- 0.5mg
- 1mg
- 5mg
capsule, extended-release (Astagraf XL)
- 0.5mg
- 1mg
- 5mg
tablet, extended-release (Envarsus XR)
- 0.75mg
- 1mg
- 4mg
injectable solution (Prograf)
- 5mg/mL
granules for oral suspension (Prograf)
- 0.2mg/packet
- 1mg/packet
Heart Transplant
Prophylaxis of organ rejection in patients receiving allogeneic transplants; use with azathioprine or mycophenolate mofetil (MMF) recommended
IV: 0.01 mg/kg/day by continuous infusion initially
PO (immediate-release): 0.075 mg/kg/day divided q12hr initially
Administer initial dose no sooner than 6 hr after transplantation
Liver Transplant
Prophylaxis of organ rejection in patients receiving allogeneic transplants
IV: 0.03-0.05 mg/kg/day by continuous infusion initially
PO (immediate-release), with corticosteroids only: 0.1-0.15 mg/kg/day divided q12hr initially
Administer initial dose no sooner than 6 hr after transplantation
Kidney Transplant
Prograf
- Prophylaxis of organ rejection in patients receiving allogeneic kidney transplants; used concomitantly with azathioprine or MMF or interleukin (IL)-2 receptor antagonist (eg, basiliximab or daclizumab) and corticosteroids
- IV: 0.03-0.05 mg/kg/day IV by continuous infusion initially
- PO (with azathioprine): 0.2 mg/kg/day divided q12hr initially
- PO (with MMF/IL-2 receptor antagonist): 0.1 mg/kg/day divided q12hr initially
Astagraf XL
- Prophylaxis of organ rejection in patients receiving kidney transplants; used concomitantly with MMF and corticosteroids, with or without basiliximab induction
-
With basiliximab induction
- MMF, corticosteroids, and initial tacrolimus dose may be administered before or within 48 hr after completion of renal transplantation but may be delayed until renal function has recovered
- 15 mg/kg PO once daily
-
Without induction
- When agent is used with MMF and corticosteroids, preoperative dose should be given as single dose within 12 hr before reperfusion; initial postoperative dose should be given ≥4 hr after preoperative dose and ≤12 hr after reperfusion
- Preoperative: 0.1 mg/kg PO once daily
- Postoperative: 0.2 mg/kg PO once daily
- Postoperative oliguria: Initial postoperative dose should be administered ≥6 hr and ≤48 hr after transplantation but may be delayed until renal function shows evidence of recovery
Envarsus XR
-
Conversion from immediate-release tacrolimus
- Indicated for prophylaxis of organ rejection in kidney transplant patients converted from tacrolimus immediate-release formulations in combination with other immunosuppressants
- Administer an Envarsus XR dose that is 80% of the total daily dose of the tacrolimus immediate-release product
- Monitor whole blood tacrolimus levels and titrate to achieve target whole blood trough concentration ranges of 4-11 ng/mL
-
De novo kidney transplant
- Indication for prophylaxis of organ rejection in de novo kidney transplant patients in combination with other immunosuppressants
- Initiate at 0.14 mg/kg/day
- Monitor whole blood tacrolimus levels and titrate to achieve target whole blood trough concentration ranges of 6-11 ng/mL (month 1) and 4-11 ng/mL (>month 1)
Lung Transplant
Prograf
Prophylaxis of organ rejection in patients receiving lung transplants in combination with other immunosuppressants
IV: 0.01-0.03 mg/kg/day by continuous infusion initially
PO (with azathioprine or MMF): 0.075 mg/kg/day divided q12hr initially
Patients with cystic fibrosis may require higher doses owing to lower bioavailability
Dosage Modifications
CYP3A5*1 allele
- African-American patients, compared to Caucasian patients, may need to be titrated to higher dosages to attain comparable trough concentrations
- ~80% of the African-American patients are carriers of the active, wild type CYP3A5*1 allele, resulting in a higher rate of tacrolimus clearance because of rapid metabolism
Coadministration with CYP3A4 inducers or inhibitors
- Dosage adjustment of Envarsus XR may be necessary
- Monitor tacrolimus trough concentrations ≥2 times on separate days during first week after initiation of dosing and after any change in dosage, after a change in coadministration of CYP3A inducers and/or inhibitors
Renal impairment
- Use lower end of dosing range
- Monitor renal function and adjust dose according to whole blood concentrations and tolerability
Hepatic impairment
- Mild: No dosage adjustment required
- Moderate: Monitor whole blood concentrations and adjust dose accordingly
- Severe (mean Child-Pugh score >10): Mean clearance of tacrolimus was substantially lower compared with normal hepatic function; dosage reduction recommended; administer 80% of preconversion daily dose of immediate release dosage form when converting from tacrolimus immediate release to extended release
Dosing Considerations
Capsules and granules are not interchangeable or substitutable with other tacrolimus extended-release products; owing to the rate of absorption following administration an extended-release tacrolimus is not equivalent to immediate-release tacrolimus drug product
Under- or overexposure to tacrolimus may result in graft rejection or other serious adverse reactions
African-American patients may need to be titrated to higher dosages to attain comparable trough concentrations compared to Caucasian patients
Monitor serum potassium
Dosage adjusted according to clinical response and observed tacrolimus whole-blood trough concentrations
-
Kidney transplant
- Trough level, Prograf with azathioprine (months 1-3): 7-20 ng/mL
- Trough level, Prograf with azathioprine (months 4-12): 5-15 ng/mL
- Trough level, Prograf with MMF/IL-2 receptor antagonist (months 1-12): 4-11 ng/mL
- Trough level, Astragraf XL with basiliximab induction (during month 1): 7-15 ng/mL
- Trough level, Astragraf XL with basiliximab induction (months 2-6): 5-15 ng/mL
- Trough level, Astragraf XL with basiliximab induction (months >6): 5-10 ng/mL
- Trough level, Astragraf XL without induction (during month 1): 10-15 ng/mL
- Trough level, Astragraf XL without induction (months 2-6): 5-15 ng/mL
- Trough level, Astragraf XL without induction (months >6): 5-10 ng/mL
- Trough level, Envarsus XR: 4-11 ng/mL
-
Liver transplant
- Trough level, Prograf with corticosteroids only (months 1-12): 5-20 ng/mL
-
Heart transplant
- Trough level, Prograf with azathioprine or MMF (months 1-3): 10-20 ng/mL
- Trough level, Prograf with azathioprine or MMF (months ≥4): 5-15 ng/mL
-
Lung transplant
- Trough level, Prograf with azathioprine or MMR (months 1-3): 10-15 ng/mL
- Trough level, Prograf with azathioprine or MMF (months ≥4): 8-12 ng/mL
Graft-Versus-Host Disease (Orphan)
Prophylaxis of GVHD
Orphan indication sponsor
- Fujisawa USA, Inc, 3 Parkway North Center, Deerfield, IL 60015
Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension (Orphan)
Orphan designation for treatment of pulmonary arterial hypertension
Sponsor
- Selten Pharma, Inc; 14435C Big Basin Way #246; Saratoga, CA 95070
Hemorrhagic Cystitis (Orphan)
Orphan designation for treatment of hemorrhagic cystitis
Sponsor
- Lipella Pharmaceuticals Inc; 400 N. Lexington Ave, LL105; Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania 15208
Dosage Forms & Strengths
capsule, immediate-release (Prograf)
- 0.5mg
- 1mg
- 5mg
injectable solution (Prograf)
- 5mg/mL
granules for oral suspension (Prograf)
- 0.2mg/packet
- 1mg/packet
Liver Transplant
Prograf
Prophylaxis of organ rejection in patients receiving liver transplants without preexisting renal or hepatic impairment
Administer initial dose no sooner than 6 hr after transplantation
IV: 0.03-0.05 mg/kg/day by continuous infusion initially
Oral
- Capsules: 0.15-0.2 mg/kg/day divided q12hr initially
- Granules: 0.2 mg/kg/day divided in 2 doses, administered q12hr initially
Heart Transplant
Prograf
Prophylaxis of organ rejection in patients receiving allogeneic transplants, in combination with other immunosuppression
Initial dose
Administer initial dose no sooner than 6 hr after transplantation
IV: 0.01 mg/kg/day by continuous infusion initially
Oral capsules and granules: 0.3 mg/kg/day divided in 2 doses, administered q12hr initially
Kidney Transplant
Prograf
Prophylaxis of organ rejection in patients receiving allogeneic transplants, in combination with other immunosuppression
Administer initial dose no sooner than 24 hr after transplantation
IV: 0.03-0.05 mg/kg/day by continuous infusion initially
Oral capsules and granules: 0.3 mg/kg/day divided in 2 doses, administered q12hr initially
Lung Transplant
Prograf
Prophylaxis of organ rejection in patients receiving lung transplants in combination with other immunosuppressants
IV: 0.01-0.03 mg/kg/day by continuous infusion initially
Oral capsules or granules: 0.03 mg/kg/day divided q12hr initially
Dosage Modifications
CYP3A5*1 allele
- African-American patients, compared to Caucasian patients, may need to be titrated to higher dosages to attain comparable trough concentrations ~80% of the African-American patients are carriers of the active, wild type CYP3A5*1 allele, resulting in a higher rate of tacrolimus clearance because of rapid metabolism
Renal impairment
- Consider using lower end of dosing range in patients who have received a liver or heart transplant and have pre-existing renal impairment; may require further dose reductions below the targeted range
- In kidney transplant patients with post-operative oliguria, administer initial dose no sooner than 6 hr and within 24 hr of transplantation, but may be delayed until renal function shows evidence of recovery
Hepatic impairment
- Mild: No dosage adjustment required
- Moderate: Monitor whole blood concentrations and adjust dose accordingly
- Severe (mean Child-Pugh score >10): Mean clearance of tacrolimus was substantially lower compared with normal hepatic function; dosage reduction recommended; administer 80% of preconversion daily dose of immediate release dosage form when converting from tacrolimus immediate release to extended release
Dosing Considerations
When converting between Prograf granules and Prograf capsules, the total daily dose should remain the same
Prograf capsules and granules are not interchangeable or substitutable with other tacrolimus extended-release products; owing to the rate of absorption following administration an extended-release tacrolimus is not equivalent to immediate-release tacrolimus drug product
Under- or overexposure to tacrolimus may result in graft rejection or other serious adverse reactions
Do not use without supervision of a physician with experience in immunosuppressive therapy
African-American patients may need to be titrated to higher dosages to attain comparable trough concentrations compared to Caucasian patients
IV formulation
- Intravenous use is recommended for patients who cannot tolerate oral formulations, and conversion from IV to PO tacrolimus is recommended as soon as oral therapy can be tolerated to minimize the risk of anaphylactic reactions that occurred with injectables containing castor oil derivatives
- Patients receiving the injection should be under continuous observation for at least the first 30 minutes following the start of the infusion and at frequent intervals thereafter
- If signs or symptoms of anaphylaxis occur, stop the infusion
- Aqueous epinephrine solution and a source of oxygen should be available at the bedside
Adjust oral dose according to clinical response and whole blood trough concentration
- Pediatric kidney, liver, or heart transplant recipients: Prograf trough level (months 1-12): 5-20 ng/mL
Pediatric lung transplant recipients: Prograf trough level (weeks 1-2: 10-20 ng/mL)
Pediatric lung transplant recipients: Prograf trough level (week 2 to month 12: 10-15 ng/mL)
-
Lung transplant recipients with cystic fibrosis
- May require higher doses to achieve target trough concentration owing to lower oral bioavailability
- Monitor and adjust dose accordingly
Interactions
Interaction Checker
No Results

Contraindicated
Serious - Use Alternative
Significant - Monitor Closely
Minor

Contraindicated (10)
- amphotericin B deoxycholate
amphotericin B deoxycholate and tacrolimus both increase nephrotoxicity and/or ototoxicity. Contraindicated.
- cidofovir
cidofovir and tacrolimus both increase nephrotoxicity and/or ototoxicity. Contraindicated.
- dronedarone
tacrolimus and dronedarone both increase QTc interval. Contraindicated.
- elagolix
tacrolimus will increase the level or effect of elagolix by Other (see comment). Contraindicated. Concomitant use of elagolix and strong OATP1B1 inhibitors is contraindicated.
- fluconazole
tacrolimus and fluconazole both increase QTc interval. Contraindicated.
- lefamulin
lefamulin will increase the level or effect of tacrolimus by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Contraindicated. Lefamulin is contraindicated with CYP3A substrates know to prolong the QT interval.
- mifepristone
mifepristone increases levels of tacrolimus by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Contraindicated. Contraindicated with CYP3A substrates that have a narrow therapeutic index .
- neomycin PO
neomycin PO and tacrolimus both increase nephrotoxicity and/or ototoxicity. Contraindicated.
- saquinavir
saquinavir will increase the level or effect of tacrolimus by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Contraindicated.
tacrolimus and saquinavir both increase QTc interval. Contraindicated. - thioridazine
tacrolimus and thioridazine both increase QTc interval. Contraindicated.
Serious - Use Alternative (228)
- adagrasib
adagrasib will increase the level or effect of tacrolimus by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Avoid coadministration of adagrasib, a CYP3A4 inhibitor, with sensitive CYP3A substrates unless otherwise recommended in the prescribing information for these substrates.
adagrasib, tacrolimus. Either increases effects of the other by QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Each drug prolongs the QTc interval, which may increased the risk of Torsade de pointes, other serious arryhthmias, and sudden death. If coadministration unavoidable, more frequent monitoring is recommended for such patients. - adalimumab
adalimumab and tacrolimus both increase immunosuppressive effects; risk of infection. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- adenovirus types 4 and 7 live, oral
tacrolimus decreases effects of adenovirus types 4 and 7 live, oral by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Immunosuppressives may diminish therapeutic effects of vaccines and increase risk of adverse effects (increased risk of infection). Live-attenuated vaccines should be avoided for at least 3mo after cessation of immunosuppressive therapy.
- afatinib
tacrolimus increases levels of afatinib by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Reduce afatinib daily dose by 10 mg if not tolerated when coadministered with P-gp inhibitors.
- alefacept
alefacept and tacrolimus both increase immunosuppressive effects; risk of infection. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- alpelisib
tacrolimus will increase the level or effect of alpelisib by Other (see comment). Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Coadministration of alpelisib (BCRP substrate) with a BCRP inhibitor may increase alpelisib concentration, which may increase the risk of toxicities. If unable to avoid or use alternant drugs, closely monitor for increased adverse reactions.
- amikacin
amikacin and tacrolimus both increase nephrotoxicity and/or ototoxicity. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- amiodarone
tacrolimus and amiodarone both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- amisulpride
amisulpride and tacrolimus both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. ECG monitoring is recommended if coadministered.
- anagrelide
tacrolimus and anagrelide both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
anagrelide and tacrolimus both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. - anakinra
anakinra and tacrolimus both increase immunosuppressive effects; risk of infection. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- anthrax vaccine
tacrolimus decreases effects of anthrax vaccine by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Contraindicated. Immunosuppressants also increase risk of infection with concomitant live vaccines.
- antithymocyte globulin equine
antithymocyte globulin equine and tacrolimus both increase immunosuppressive effects; risk of infection. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- antithymocyte globulin rabbit
antithymocyte globulin rabbit and tacrolimus both increase immunosuppressive effects; risk of infection. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- apalutamide
apalutamide will decrease the level or effect of tacrolimus by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Coadministration of apalutamide, a strong CYP3A4 inducer, with drugs that are CYP3A4 substrates can result in lower exposure to these medications. Avoid or substitute another drug for these medications when possible. Evaluate for loss of therapeutic effect if medication must be coadministered. Adjust dose according to prescribing information if needed.
- arsenic trioxide
tacrolimus and arsenic trioxide both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- artemether
artemether and tacrolimus both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- artemether/lumefantrine
tacrolimus and artemether/lumefantrine both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- asenapine
tacrolimus and asenapine both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
asenapine and tacrolimus both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. - asenapine transdermal
asenapine transdermal and tacrolimus both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- axicabtagene ciloleucel
tacrolimus, axicabtagene ciloleucel. Either increases effects of the other by immunosuppressive effects; risk of infection. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- azathioprine
azathioprine and tacrolimus both increase immunosuppressive effects; risk of infection. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- azithromycin
tacrolimus and azithromycin both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- bacitracin
tacrolimus and bacitracin both increase nephrotoxicity and/or ototoxicity. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Avoid concurrent use of bacitracin with other nephrotoxic drugs
- baricitinib
baricitinib, tacrolimus. Either increases toxicity of the other by immunosuppressive effects; risk of infection. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Baricitinib is not recommended in combination with other JAK inhibitors, biologic DMARDs, or potent immunosuppressives.
- basiliximab
basiliximab and tacrolimus both increase immunosuppressive effects; risk of infection. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- BCG vaccine live
tacrolimus decreases effects of BCG vaccine live by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Contraindicated. Immunosuppressants also increase risk of infection with concomitant live vaccines.
- bosutinib
tacrolimus increases levels of bosutinib by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- bremelanotide
bremelanotide will decrease the level or effect of tacrolimus by Other (see comment). Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Bremelanotide may slow gastric emptying and potentially reduces the rate and extent of absorption of concomitantly administered oral medications. Avoid use when taking any oral drug that is dependent on threshold concentrations for efficacy. Interactions listed are representative examples and do not include all possible clinical examples.
- brexucabtagene autoleucel
tacrolimus, brexucabtagene autoleucel. Either increases effects of the other by immunosuppressive effects; risk of infection. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- brigatinib
brigatinib will decrease the level or effect of tacrolimus by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Brigatinib induces CYP3A4 in vitro. Coadministration with CYP3A4 substrates, particularly those with a narrow therapeutic index, can result in decreased concentrations and loss of efficacy. If unable to avoid coadministration, monitor CYP3A4 substrate levels and adjust dose as needed.
- buprenorphine
tacrolimus and buprenorphine both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- buprenorphine buccal
buprenorphine buccal and tacrolimus both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- buprenorphine subdermal implant
buprenorphine subdermal implant and tacrolimus both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- buprenorphine transdermal
buprenorphine transdermal and tacrolimus both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- buprenorphine, long-acting injection
buprenorphine, long-acting injection and tacrolimus both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- canakinumab
canakinumab and tacrolimus both increase immunosuppressive effects; risk of infection. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- carbamazepine
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of tacrolimus by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Monitor tacrolimus levels and adjust dose accordingly
- ceritinib
ceritinib increases levels of tacrolimus by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Avoid concurrent use of CYP3A substrates known to have narrow therapeutic indices or substrates primarily metabolized by CYP3A during treatment with ceritinib; if use of these medications is unavoidable, consider dose.
ceritinib and tacrolimus both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. - chloramphenicol
chloramphenicol will increase the level or effect of tacrolimus by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- chlorpromazine
tacrolimus and chlorpromazine both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- ciltacabtagene autoleucel
tacrolimus, ciltacabtagene autoleucel. Either increases effects of the other by immunosuppressive effects; risk of infection. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- cimetidine
cimetidine will increase the level or effect of tacrolimus by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- clarithromycin
clarithromycin will increase the level or effect of tacrolimus by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
clarithromycin and tacrolimus both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. - contrast media (iodinated)
contrast media (iodinated) and tacrolimus both increase nephrotoxicity and/or ototoxicity. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- crizotinib
crizotinib increases levels of tacrolimus by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Coadministration of crizotinib with CYP3A substrates with narrow therapeutic indices should be avoided. ECG monitoring is recommended, along with drugs that may prolong the QT interval.
crizotinib and tacrolimus both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. - cyclosporine
cyclosporine, tacrolimus. Other (see comment). Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Comment: Coadministration of tacrolimus with cyclosporine may increase the risk of nephrotoxicity and immunosuppressive effects. Additionally, both agents are CYP3A4 and P-gp substrates and may elevate serum levels of either agent when coadministered. Discontinue tacrolimus or cyclosporine therapy at least 24 hours before initiating therapy with the other agent.
- dabrafenib
dabrafenib will decrease the level or effect of tacrolimus by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
tacrolimus and dabrafenib both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. - danazol
danazol will increase the level or effect of tacrolimus by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- desflurane
desflurane and tacrolimus both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- diclofenac
diclofenac, tacrolimus. Either increases toxicity of the other by Other (see comment). Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Comment: Concomitant administration increases risk of nephrotoxicity.
- diflunisal
diflunisal, tacrolimus. Either increases toxicity of the other by Other (see comment). Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Comment: Concomitant administration increases risk of nephrotoxicity.
- diphtheria & tetanus toxoids
tacrolimus decreases effects of diphtheria & tetanus toxoids by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Contraindicated. Immunosuppressants also increase risk of infection with concomitant live vaccines.
- diphtheria & tetanus toxoids/ acellular pertussis vaccine
tacrolimus decreases effects of diphtheria & tetanus toxoids/ acellular pertussis vaccine by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Contraindicated. Immunosuppressants also increase risk of infection with concomitant live vaccines.
- diphtheria & tetanus toxoids/acellular pertussis/poliovirus, inactivated vaccine
tacrolimus decreases effects of diphtheria & tetanus toxoids/acellular pertussis/poliovirus, inactivated vaccine by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Contraindicated. Immunosuppressants also increase risk of infection with concomitant live vaccines.
- disopyramide
tacrolimus and disopyramide both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- dronedarone
dronedarone will increase the level or effect of tacrolimus by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. The use of dronedarone in combination with other medications that can prolong the QT interval is considered contraindicated.
- droperidol
tacrolimus and droperidol both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- edoxaban
tacrolimus will increase the level or effect of edoxaban by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Dose adjustment may be required with strong P-gp inhibitors. DVT/PE treatment: Decrease dose to 30 mg PO once daily. NVAF: No dose reduction recommended
- efavirenz
efavirenz will decrease the level or effect of tacrolimus by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- eluxadoline
tacrolimus increases levels of eluxadoline by decreasing metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Decrease eluxadoline dose to 75 mg PO BID if coadministered with OATP1B1 inhibitors. .
- encorafenib
encorafenib and tacrolimus both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- entrectinib
entrectinib and tacrolimus both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- enzalutamide
enzalutamide will decrease the level or effect of tacrolimus by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- erdafitinib
erdafitinib, tacrolimus. affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Avoid coadministration with erdafitinib and sensitive CYP3A4 substrates with narrow therapeutic indices. Erdafitinib may altered plasma concentrations of CYP3A4 substrates, leading to either loss of activity or increased toxicity of the substrate.
erdafitinib will increase the level or effect of tacrolimus by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. If coadministration unavoidable, separate administration by at least 6 hr before or after administration of P-gp substrates with narrow therapeutic index. - eribulin
eribulin and tacrolimus both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- erythromycin base
erythromycin base will increase the level or effect of tacrolimus by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
tacrolimus and erythromycin base both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. - erythromycin ethylsuccinate
erythromycin ethylsuccinate will increase the level or effect of tacrolimus by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
tacrolimus and erythromycin ethylsuccinate both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. - erythromycin lactobionate
erythromycin lactobionate will increase the level or effect of tacrolimus by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
tacrolimus and erythromycin lactobionate both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. - erythromycin stearate
erythromycin stearate will increase the level or effect of tacrolimus by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
tacrolimus and erythromycin stearate both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. - etanercept
etanercept and tacrolimus both increase immunosuppressive effects; risk of infection. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- etodolac
etodolac, tacrolimus. Either increases toxicity of the other by Other (see comment). Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Comment: Concomitant administration increases risk of nephrotoxicity.
- etrasimod
etrasimod, tacrolimus. Either increases effects of the other by Mechanism: aldehyde dehydrogenase inhibition. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Risk of additive immune system effects with etrasimod has not been studied in combination with antineoplastic, immune-modulating, or noncorticosteroid immunosuppressive therapies. Avoid coadministration during and in the weeks following administration of etrasimod.
- fenoprofen
fenoprofen, tacrolimus. Either increases toxicity of the other by Other (see comment). Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Comment: Concomitant administration increases risk of nephrotoxicity.
- fexinidazole
fexinidazole and tacrolimus both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Avoid coadministration of fexinidazole with drugs known to block potassium channels or prolong QT interval.
fexinidazole will increase the level or effect of tacrolimus by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Fexinidazole inhibits CYP3A4. Coadministration may increase risk for adverse effects of CYP3A4 substrates. - flecainide
tacrolimus and flecainide both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- flurbiprofen
flurbiprofen, tacrolimus. Either increases toxicity of the other by Other (see comment). Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Comment: Concomitant administration increases risk of nephrotoxicity.
- foscarnet
tacrolimus and foscarnet both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- glasdegib
tacrolimus and glasdegib both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- glatiramer
glatiramer and tacrolimus both increase immunosuppressive effects; risk of infection. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- golimumab
golimumab and tacrolimus both increase immunosuppressive effects; risk of infection. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- hepatitis A vaccine inactivated
tacrolimus decreases effects of hepatitis A vaccine inactivated by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Contraindicated. Immunosuppressants also increase risk of infection with concomitant live vaccines.
- hepatitis a/b vaccine
tacrolimus decreases effects of hepatitis a/b vaccine by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Contraindicated. Immunosuppressants also increase risk of infection with concomitant live vaccines.
- hepatitis a/typhoid vaccine
tacrolimus decreases effects of hepatitis a/typhoid vaccine by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Contraindicated. Immunosuppressants also increase risk of infection with concomitant live vaccines.
- hepatitis b vaccine
tacrolimus decreases effects of hepatitis b vaccine by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Contraindicated. Immunosuppressants also increase risk of infection with concomitant live vaccines.
- human papillomavirus vaccine, nonavalent
tacrolimus decreases effects of human papillomavirus vaccine, nonavalent by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Immunosuppressive therapies, including irradiation, antimetabolites, alkylating agents, cytotoxic drugs, and corticosteroids (used in greater than physiologic doses), may reduce the immune responses to vaccines.
- human papillomavirus vaccine, quadrivalent
tacrolimus decreases effects of human papillomavirus vaccine, quadrivalent by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Immunosuppressive therapies, including irradiation, antimetabolites, alkylating agents, cytotoxic drugs, and corticosteroids (used in greater than physiologic doses), may reduce the immune responses to vaccines.
- hydroxychloroquine sulfate
hydroxychloroquine sulfate and tacrolimus both increase immunosuppressive effects; risk of infection. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
hydroxychloroquine sulfate and tacrolimus both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. - ibuprofen
ibuprofen, tacrolimus. Either increases toxicity of the other by Other (see comment). Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Comment: Concomitant administration increases risk of nephrotoxicity.
- ibuprofen IV
ibuprofen IV, tacrolimus. Either increases toxicity of the other by Other (see comment). Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Comment: Concomitant administration increases risk of nephrotoxicity.
- ibutilide
tacrolimus and ibutilide both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- idecabtagene vicleucel
tacrolimus, idecabtagene vicleucel. Either increases effects of the other by immunosuppressive effects; risk of infection. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- idelalisib
idelalisib will increase the level or effect of tacrolimus by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Idelalisib is a strong CYP3A inhibitor; avoid coadministration with sensitive CYP3A substrates
- ifosfamide
ifosfamide, tacrolimus. Either increases effects of the other by immunosuppressive effects; risk of infection. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- iloperidone
tacrolimus and iloperidone both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- indomethacin
indomethacin, tacrolimus. Either increases toxicity of the other by Other (see comment). Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Comment: Concomitant administration increases risk of nephrotoxicity.
- infliximab
infliximab and tacrolimus both increase immunosuppressive effects; risk of infection. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- influenza virus vaccine quadrivalent
tacrolimus decreases effects of influenza virus vaccine quadrivalent by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Contraindicated. Immunosuppressants also increase risk of infection with concomitant live vaccines.
- influenza virus vaccine quadrivalent, adjuvanted
tacrolimus decreases effects of influenza virus vaccine quadrivalent, adjuvanted by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Immunosuppressive drugs may reduce the immune response to influenza vaccine.
- influenza virus vaccine quadrivalent, cell-cultured
tacrolimus decreases effects of influenza virus vaccine quadrivalent, cell-cultured by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Contraindicated. Immunosuppressants also increase risk of infection with concomitant live vaccines.
- influenza virus vaccine quadrivalent, intranasal
tacrolimus decreases effects of influenza virus vaccine quadrivalent, intranasal by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Contraindicated. Immunosuppressants also increase risk of infection with concomitant live vaccines.
- influenza virus vaccine trivalent
tacrolimus decreases effects of influenza virus vaccine trivalent by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Contraindicated. Immunosuppressants also increase risk of infection with concomitant live vaccines.
- influenza virus vaccine trivalent, adjuvanted
tacrolimus decreases effects of influenza virus vaccine trivalent, adjuvanted by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Immunosuppressive drugs may reduce the immune response to influenza vaccine.
- inotuzumab
tacrolimus and inotuzumab both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- ioversol
ioversol and tacrolimus both increase nephrotoxicity and/or ototoxicity. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- isoflurane
isoflurane and tacrolimus both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- itraconazole
itraconazole and tacrolimus both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- ivosidenib
ivosidenib and tacrolimus both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Avoid coadministration of QTc prolonging drugs with ivosidenib or replace with alternate therapies. If coadministration of a QTc prolonging drug is unavoidable, monitor for increased risk of QTc interval prolongation.
ivosidenib will decrease the level or effect of tacrolimus by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Avoid coadministration of sensitive CYP3A4 substrates with ivosidenib or replace with alternative therapies. If coadministration is unavoidable, monitor patients for loss of therapeutic effect of these drugs. - Japanese encephalitis virus vaccine
tacrolimus decreases effects of Japanese encephalitis virus vaccine by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Contraindicated. Immunosuppressants also increase risk of infection with concomitant live vaccines.
- ketoconazole
ketoconazole will increase the level or effect of tacrolimus by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- ketoprofen
ketoprofen, tacrolimus. Either increases toxicity of the other by Other (see comment). Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Comment: Concomitant administration increases risk of nephrotoxicity.
- ketorolac
ketorolac, tacrolimus. Either increases toxicity of the other by Other (see comment). Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Comment: Concomitant administration increases risk of nephrotoxicity.
- lapatinib
tacrolimus and lapatinib both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- lasmiditan
lasmiditan increases levels of tacrolimus by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- lefamulin
tacrolimus and lefamulin both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- leflunomide
leflunomide and tacrolimus both increase immunosuppressive effects; risk of infection. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- lenvatinib
tacrolimus and lenvatinib both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- levoketoconazole
levoketoconazole will increase the level or effect of tacrolimus by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- lisocabtagene maraleucel
tacrolimus, lisocabtagene maraleucel. Either increases effects of the other by immunosuppressive effects; risk of infection. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- lofexidine
tacrolimus and lofexidine both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- lonafarnib
lonafarnib will increase the level or effect of tacrolimus by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Avoid coadministration with sensitive CYP3A substrates. If coadministration unavoidable, monitor for adverse reactions and reduce CYP3A substrate dose in accordance with product labeling.
- lopinavir
lopinavir will increase the level or effect of tacrolimus by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
tacrolimus and lopinavir both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. - lorlatinib
lorlatinib will decrease the level or effect of tacrolimus by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Avoid use of lorlatinib with CYP3A substrates, where minimal concentration changes may lead to serious therapeutic failures of the substrate. If concomitant use is unavoidable, increase CYP3A substrate dosage in accordance with approved product labeling.
- lumacaftor/ivacaftor
lumacaftor/ivacaftor will decrease the level or effect of tacrolimus by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Lumacaftor is a strong inducer of CYP3A. Avoid coadministration with sensitive CYP3A substrates or CYP3A substrates with a narrow therapeutic index.
- macimorelin
macimorelin and tacrolimus both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Macimorelin causes an increase of ~11 msec in the corrected QT interval. Avoid coadministration with drugs that prolong QT interval, which could increase risk for developing torsade de pointes-type ventricular tachycardia. Allow sufficient washout time of drugs that are known to prolong the QT interval before administering macimorelin.
- measles (rubeola) vaccine
tacrolimus decreases effects of measles (rubeola) vaccine by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Contraindicated. Immunosuppressants also increase risk of infection with concomitant live vaccines.
- measles mumps and rubella vaccine, live
tacrolimus decreases effects of measles mumps and rubella vaccine, live by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Contraindicated. Immunosuppressants also increase risk of infection with concomitant live vaccines.
- measles, mumps, rubella and varicella vaccine, live
tacrolimus decreases effects of measles, mumps, rubella and varicella vaccine, live by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Contraindicated. Immunosuppressants also increase risk of infection with concomitant live vaccines.
- meclofenamate
meclofenamate, tacrolimus. Either increases toxicity of the other by Other (see comment). Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Comment: Concomitant administration increases risk of nephrotoxicity.
- mefenamic acid
mefenamic acid, tacrolimus. Either increases toxicity of the other by Other (see comment). Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Comment: Concomitant administration increases risk of nephrotoxicity.
- mefloquine
mefloquine increases toxicity of tacrolimus by QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Mefloquine may enhance the QTc prolonging effect of high risk QTc prolonging agents.
- meloxicam
meloxicam, tacrolimus. Either increases toxicity of the other by Other (see comment). Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Comment: Concomitant administration increases risk of nephrotoxicity.
- melphalan
melphalan, tacrolimus. Either decreases effects of the other by immunosuppressive effects; risk of infection. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Concomitant therapy is expected to increase the risk of immunosuppression. Use caution when switching patients from long-acting therapies with immune effects.
- meningococcal A C Y and W-135 polysaccharide vaccine combined
tacrolimus decreases effects of meningococcal A C Y and W-135 polysaccharide vaccine combined by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Contraindicated. Immunosuppressants also increase risk of infection with concomitant live vaccines.
- methadone
tacrolimus and methadone both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- midostaurin
tacrolimus and midostaurin both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- mobocertinib
mobocertinib will decrease the level or effect of tacrolimus by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. If use is unavoidable, increase CYP3A4 substrate dosage in accordance with its prescribing information.
mobocertinib and tacrolimus both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. If coadministration unavoidable, reduce mobocertinib dose and monitor QTc interval more frequently. - moxifloxacin
tacrolimus and moxifloxacin both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- muromonab CD3
muromonab CD3 and tacrolimus both increase immunosuppressive effects; risk of infection. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- mycophenolate
mycophenolate and tacrolimus both increase immunosuppressive effects; risk of infection. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- nabumetone
nabumetone, tacrolimus. Either increases toxicity of the other by Other (see comment). Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Comment: Concomitant administration increases risk of nephrotoxicity.
- naproxen
naproxen, tacrolimus. Either increases toxicity of the other by Other (see comment). Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Comment: Concomitant administration increases risk of nephrotoxicity.
- nefazodone
nefazodone will increase the level or effect of tacrolimus by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- nilotinib
tacrolimus and nilotinib both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- nirmatrelvir
nirmatrelvir will increase the level or effect of tacrolimus by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. If unable to avoid, decrease tacrolimus dose by one-third. Strong CYP3A inhibitors may increase tacrolimus whole blood trough concentrations and increase risk of serious adverse reactions (eg, neurotoxicity, QT prolongation). A rapid, sharp rise in tacrolimus levels may occur early, despite an immediate reduction of tacrolimus dose.
- nirmatrelvir/ritonavir
nirmatrelvir/ritonavir will increase the level or effect of tacrolimus by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. If unable to avoid, decrease tacrolimus dose by one-third. Strong CYP3A inhibitors may increase tacrolimus whole blood trough concentrations and increase risk of serious adverse reactions (eg, neurotoxicity, QT prolongation). A rapid, sharp rise in tacrolimus levels may occur early, despite an immediate reduction of tacrolimus dose.
- olutasidenib
olutasidenib will decrease the level or effect of tacrolimus by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Avoid coadministration of olutasidenib (a CYP3A4 inducer) with sensitive CYP3A substrates unless otherwise instructed in substrates prescribing information. If unavoidable, monitor for loss of therapeutic effect of sensitive CYP3A4 substrates.
- ondansetron
ondansetron and tacrolimus both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Avoid with congenital long QT syndrome; ECG monitoring recommended with concomitant medications that prolong QT interval, electrolyte abnormalities, CHF, or bradyarrhythmias.
- oxaliplatin
oxaliplatin and tacrolimus both increase immunosuppressive effects; risk of infection. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Concomitant therapy is expected to increase the risk of immunosuppression. Use caution when switching patients from long-acting therapies with immune effects.
oxaliplatin and tacrolimus both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. - oxaprozin
oxaprozin, tacrolimus. Either increases toxicity of the other by Other (see comment). Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Comment: Concomitant administration increases risk of nephrotoxicity.
- pacritinib
pacritinib will increase the level or effect of tacrolimus by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- paliperidone
tacrolimus and paliperidone both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- panobinostat
tacrolimus and panobinostat both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- pasireotide
tacrolimus and pasireotide both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- pazopanib
tacrolimus and pazopanib both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- pentamidine
tacrolimus and pentamidine both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- pexidartinib
pexidartinib will decrease the level or effect of tacrolimus by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Coadministration of pexidartinib (a CYP3A4 inducer) with sensitive CYP3A substrates may lead to serious therapeutic failures. If concomitant use is unavoidable, increase the CYP3A substrate dosage in accordance with approved product labeling.
- pimavanserin
tacrolimus and pimavanserin both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- pimozide
tacrolimus and pimozide both increase QTc interval. Contraindicated.
- piroxicam
piroxicam, tacrolimus. Either increases toxicity of the other by Other (see comment). Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Comment: Concomitant administration increases risk of nephrotoxicity.
- pitolisant
tacrolimus and pitolisant both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- pneumococcal vaccine 13-valent
tacrolimus decreases effects of pneumococcal vaccine 13-valent by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Contraindicated. Immunosuppressants also increase risk of infection with concomitant live vaccines.
- pneumococcal vaccine heptavalent
tacrolimus decreases effects of pneumococcal vaccine heptavalent by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Contraindicated. Immunosuppressants also increase risk of infection with concomitant live vaccines.
- pneumococcal vaccine polyvalent
tacrolimus decreases effects of pneumococcal vaccine polyvalent by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Contraindicated. Immunosuppressants also increase risk of infection with concomitant live vaccines.
- pomalidomide
tacrolimus increases levels of pomalidomide by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- ponesimod
tacrolimus and ponesimod both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- posaconazole
tacrolimus and posaconazole both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- potassium phosphates, IV
tacrolimus and potassium phosphates, IV both increase serum potassium. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- procainamide
tacrolimus and procainamide both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- propafenone
tacrolimus and propafenone both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- protriptyline
tacrolimus and protriptyline both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- quinidine
quinidine will increase the level or effect of tacrolimus by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
tacrolimus and quinidine both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. - rabies vaccine
tacrolimus decreases effects of rabies vaccine by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Contraindicated. Immunosuppressants may interfere with development of active immunity.
- rabies vaccine chick embryo cell derived
tacrolimus decreases effects of rabies vaccine chick embryo cell derived by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Contraindicated. Immunosuppressants also increase risk of infection with concomitant live vaccines.
- ranolazine
tacrolimus and ranolazine both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- repotrectinib
tacrolimus will increase the level or effect of repotrectinib by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
repotrectinib will decrease the level or effect of tacrolimus by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Repotrectinib is a CYP3A4 inducer. Avoid coadministration with CYP3A substrates where minimal concentration changes can cause reduced efficacy, unless otherwise recommended their prescribing information. - revefenacin
tacrolimus increases levels of revefenacin by Other (see comment). Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Comment: OATP1B1 and OATP1B3 transport inhibitors may increase systemic exposure of revefenacin's active metabolite. Coadministration not recommended.
- ribociclib
ribociclib increases toxicity of tacrolimus by QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- rifabutin
rifabutin will decrease the level or effect of tacrolimus by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- rifampin
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of tacrolimus by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- rilonacept
rilonacept and tacrolimus both increase immunosuppressive effects; risk of infection. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- rimegepant
tacrolimus will increase the level or effect of rimegepant by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- riociguat
tacrolimus will increase the level or effect of riociguat by decreasing metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Coadministration of riociguat (substrate of CYP isoenzymes 1A1, 2C8, 3A, 2J2) with strong CYP inhibitors may require a decreased initial dose of 0.5 mg PO TID; monitor for signs of hypotension and reduce dose if needed
- romidepsin
tacrolimus and romidepsin both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- ropeginterferon alfa 2b
ropeginterferon alfa 2b, tacrolimus. Either increases toxicity of the other by Other (see comment). Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Comment: Myelosuppressive agents can produce additive myelosuppression. Avoid use and monitor patients receiving the combination for effects of excessive myelosuppression.
- rotavirus oral vaccine, live
tacrolimus decreases effects of rotavirus oral vaccine, live by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Contraindicated. Immunosuppressants also increase risk of infection with concomitant live vaccines.
- rubella vaccine
tacrolimus decreases effects of rubella vaccine by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Contraindicated. Immunosuppressants also increase risk of infection with concomitant live vaccines.
- sevoflurane
sevoflurane and tacrolimus both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- siponimod
siponimod and tacrolimus both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- sirolimus
sirolimus and tacrolimus both increase immunosuppressive effects; risk of infection. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- smallpox (vaccinia) vaccine, live
tacrolimus decreases effects of smallpox (vaccinia) vaccine, live by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Contraindicated. Immunosuppressants also increase risk of infection with concomitant live vaccines.
- sotalol
tacrolimus and sotalol both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- sotorasib
sotorasib will decrease the level or effect of tacrolimus by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. If use is unavoidable, refer to the prescribing information of the CYP3A4 substrate for dosage modifications
sotorasib will decrease the level or effect of tacrolimus by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. If use is unavoidable, refer to the prescribing information of the P-gp substrate for dosage modifications. - St John's Wort
St John's Wort will decrease the level or effect of tacrolimus by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
St John's Wort decreases levels of tacrolimus by increasing metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. - sulbactam/durlobactam
tacrolimus will increase the level or effect of sulbactam/durlobactam by Other (see comment). Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Sulbactam is predicted to have active secretion by OATP1 as a significant portion of total clearance; therefore, inhibition of OAT1 may increase sulbactam plasma concentrations
- sulindac
sulindac, tacrolimus. Either increases toxicity of the other by Other (see comment). Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Comment: Concomitant administration increases risk of nephrotoxicity.
- teicoplanin
tacrolimus and teicoplanin both increase nephrotoxicity and/or ototoxicity. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- telavancin
tacrolimus and telavancin both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- temsirolimus
tacrolimus and temsirolimus both increase immunosuppressive effects; risk of infection. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- tetanus toxoid adsorbed or fluid
tacrolimus decreases effects of tetanus toxoid adsorbed or fluid by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Contraindicated. Immunosuppressants also increase risk of infection with concomitant live vaccines.
- tetrabenazine
tacrolimus and tetrabenazine both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- tick-borne encephalitis vaccine
tacrolimus decreases effects of tick-borne encephalitis vaccine by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Contraindicated. Immunosuppressants also increase risk of infection with concomitant live vaccines.
- tipranavir
tipranavir will increase the level or effect of tacrolimus by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- tisagenlecleucel
tacrolimus, tisagenlecleucel. Either increases effects of the other by immunosuppressive effects; risk of infection. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- tocilizumab
tocilizumab and tacrolimus both increase immunosuppressive effects; risk of infection. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- tofacitinib
tacrolimus, tofacitinib. Either increases toxicity of the other by immunosuppressive effects; risk of infection. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- tolmetin
tolmetin, tacrolimus. Either increases toxicity of the other by Other (see comment). Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Comment: Concomitant administration increases risk of nephrotoxicity.
- tongkat ali
tacrolimus and tongkat ali both increase immunosuppressive effects; risk of infection. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- topotecan
tacrolimus will increase the level or effect of topotecan by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Product labeling for PO topotecan recommends avoiding concomitant use of P-gp inhibitors; the interaction with IV topotecan may be less severe but is still likely of clinical significance
- toremifene
tacrolimus and toremifene both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Concurrent use of toremifene with agents causing QT prolongation should be avoided. If concomitant use is required it's recommended that toremifene be interrupted. If interruption not possible, patients requiring therapy with a drug that prolongs QT should be closely monitored. ECGs should be obtained for high risk patients.
- travelers diarrhea and cholera vaccine inactivated
tacrolimus decreases effects of travelers diarrhea and cholera vaccine inactivated by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Contraindicated. Immunosuppressants also increase risk of infection with concomitant live vaccines.
- trazodone
tacrolimus and trazodone both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- tucatinib
tucatinib will increase the level or effect of tacrolimus by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Avoid concomitant use of tucatinib with CYP3A substrates, where minimal concentration changes may lead to serious or life-threatening toxicities. If unavoidable, reduce CYP3A substrate dose according to product labeling.
- typhoid polysaccharide vaccine
tacrolimus decreases effects of typhoid polysaccharide vaccine by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Contraindicated. Immunosuppressants also increase risk of infection with concomitant live vaccines.
- typhoid vaccine live
tacrolimus decreases effects of typhoid vaccine live by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Contraindicated. Immunosuppressants also increase risk of infection with concomitant live vaccines.
- umeclidinium bromide/vilanterol inhaled
tacrolimus increases toxicity of umeclidinium bromide/vilanterol inhaled by QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Exercise extreme caution when vilanterol coadministered with drugs that prolong QTc interval; adrenergic agonist effects on the cardiovascular system may be potentiated.
- upadacitinib
tacrolimus, upadacitinib. Either increases effects of the other by immunosuppressive effects; risk of infection. Contraindicated.
- ustekinumab
tacrolimus and ustekinumab both increase immunosuppressive effects; risk of infection. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- vandetanib
tacrolimus, vandetanib. Either increases toxicity of the other by QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Avoid coadministration with drugs known to prolong QT interval; if a drug known to prolong QT interval must be used, more frequent ECG monitoring is recommended.
- varicella virus vaccine live
tacrolimus decreases effects of varicella virus vaccine live by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Contraindicated. Immunosuppressants also increase risk of infection with concomitant live vaccines.
- vemurafenib
tacrolimus and vemurafenib both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- venetoclax
tacrolimus will increase the level or effect of venetoclax by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. If a P-gp inhibitor must be used, reduce the venetoclax dose by at least 50%. Monitor more closely for signs of venetoclax toxicities.
venetoclax will increase the level or effect of tacrolimus by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. In vitro data suggest venetoclax may inhibit P-gp substrates at therapeutic dose levels in the gut. Avoid coadministration of narrow therapeutic index P-gp substrates with venetoclax. If a narrow therapeutic index P-gp substrate must be used, it should be taken at least 6 hr before venetoclax. - vilanterol/fluticasone furoate inhaled
tacrolimus increases toxicity of vilanterol/fluticasone furoate inhaled by QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Exercise extreme caution when vilanterol coadministered with drugs that prolong QTc interval; adrenergic agonist effects on the cardiovascular system may be potentiated.
- voriconazole
tacrolimus and voriconazole both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- voxelotor
voxelotor will increase the level or effect of tacrolimus by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Voxelotor increases systemic exposure of sensitive CYP3A4 substrates. Avoid coadministration with sensitive CYP3A4 substrates with a narrow therapeutic index. Consider dose reduction of the sensitive CYP3A4 substrate(s) if unable to avoid.
- yellow fever vaccine
tacrolimus decreases effects of yellow fever vaccine by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Contraindicated. Immunosuppressants also increase risk of infection with concomitant live vaccines.
- ziprasidone
tacrolimus and ziprasidone both increase QTc interval. Contraindicated.
- zoster vaccine live
tacrolimus decreases effects of zoster vaccine live by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Contraindicated. Immunosuppressants also increase risk of infection with concomitant live vaccines.
Monitor Closely (348)
- acyclovir
acyclovir and tacrolimus both increase nephrotoxicity and/or ototoxicity. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- adefovir
adefovir and tacrolimus both increase nephrotoxicity and/or ototoxicity. Use Caution/Monitor.
- albuterol
albuterol and tacrolimus both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
- alfuzosin
tacrolimus and alfuzosin both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
alfuzosin and tacrolimus both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor. - amikacin
tacrolimus will increase the level or effect of amikacin by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor.
- amiodarone
amiodarone will increase the level or effect of tacrolimus by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor.
- amitriptyline
tacrolimus will increase the level or effect of amitriptyline by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor.
- amlodipine
amlodipine will increase the level or effect of tacrolimus by unspecified interaction mechanism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Adjust dose when appropriate.
- amobarbital
amobarbital will decrease the level or effect of tacrolimus by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- apomorphine
apomorphine and tacrolimus both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
- aprepitant
aprepitant will increase the level or effect of tacrolimus by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- arformoterol
arformoterol and tacrolimus both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
- aripiprazole
aripiprazole and tacrolimus both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
- armodafinil
armodafinil will decrease the level or effect of tacrolimus by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- artemether/lumefantrine
artemether/lumefantrine will decrease the level or effect of tacrolimus by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- astragalus
tacrolimus increases and astragalus decreases immunosuppressive effects; risk of infection. Effect of interaction is not clear, use caution. Use Caution/Monitor.
- atazanavir
atazanavir will increase the level or effect of tacrolimus by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- atogepant
tacrolimus will increase the level or effect of atogepant by Other (see comment). Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Recommended dosage of atogepant (an OATP1B1 substrate) with concomitant use of OATP inhibitors is 10 mg or 30 mg qDay.
- atomoxetine
atomoxetine and tacrolimus both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
- atorvastatin
atorvastatin will increase the level or effect of tacrolimus by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor.
tacrolimus increases toxicity of atorvastatin by Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor. Comment: OATP1B1 inhibitors may increase risk of myopathy. - azithromycin
azithromycin will increase the level or effect of tacrolimus by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor.
- bazedoxifene/conjugated estrogens
tacrolimus will increase the level or effect of bazedoxifene/conjugated estrogens by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor.
- bedaquiline
tacrolimus and bedaquiline both increase QTc interval. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. ECG should be monitored closely
- belatacept
belatacept and tacrolimus both increase immunosuppressive effects; risk of infection. Use Caution/Monitor.
- berotralstat
berotralstat will increase the level or effect of tacrolimus by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor. Monitor or titrate P-gp substrate dose if coadministered.
berotralstat will increase the level or effect of tacrolimus by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Monitor or titrate substrate dose when berotralstat is coadministered with narrow therapeutic index drugs that are CYP3A substrates. - betrixaban
tacrolimus increases levels of betrixaban by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor. Decrease betrixaban dose to 80 mg PO once, then 40 mg PO qDay if coadministered with a P-gp inhibitor.
- blinatumomab
blinatumomab increases levels of tacrolimus by decreasing metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Treatment initiation causes transient release of cytokines that may suppress CYP450 enzymes; highest drug-drug interaction risk is during the first 9 days of the first cycle and the first 2 days of the 2nd cycle in patients who are receiving concomitant CYP450 substrates, particularly those with a narrow therapeutic index.
- bosentan
bosentan will decrease the level or effect of tacrolimus by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- bosutinib
bosutinib increases levels of tacrolimus by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor.
- brodalumab
brodalumab, tacrolimus. Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor. Comment: Formation of CYP450 enzymes can be altered by increased levels of certain cytokines during chronic inflammation; thus, brodalumab could normalize the formation of CYP450 enzymes. Upon initiation or discontinuation of brodalumab in patients who are receiving concomitant CYP450 substrates, particularly those with a narrow therapeutic index, consider monitoring for therapeutic effect.
- bromocriptine
bromocriptine increases levels of tacrolimus by decreasing metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- budesonide
budesonide will decrease the level or effect of tacrolimus by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
tacrolimus will increase the level or effect of budesonide by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor. - butabarbital
butabarbital will decrease the level or effect of tacrolimus by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- butalbital
butalbital will decrease the level or effect of tacrolimus by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- canagliflozin
tacrolimus and canagliflozin both increase serum potassium. Use Caution/Monitor.
- cannabidiol
cannabidiol will increase the level or effect of tacrolimus by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor. Therapeutic drug monitoring and dose reduction of P-gp substrates should be considered when given orally and concurrently with cannabidiol
- capreomycin
capreomycin and tacrolimus both increase nephrotoxicity and/or ototoxicity. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- carboplatin
carboplatin and tacrolimus both increase nephrotoxicity and/or ototoxicity. Use Caution/Monitor.
- cenobamate
cenobamate will decrease the level or effect of tacrolimus by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Increase dose of CYP3A4 substrate, as needed, when coadministered with cenobamate.
- cephaloridine
cephaloridine and tacrolimus both increase nephrotoxicity and/or ototoxicity. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- ceritinib
tacrolimus increases levels of ceritinib by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor.
- chloroquine
chloroquine increases toxicity of tacrolimus by QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
- cholera vaccine
tacrolimus decreases effects of cholera vaccine by immunosuppressive effects; risk of infection. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Immunosuppressive therapies, including irradiation, antimetabolites, alkylating agents, cytotoxic drugs and corticosteroids (used in greater than physiologic doses), may reduce the immune response to cholera vaccine.
- ciprofloxacin
tacrolimus and ciprofloxacin both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
- cisplatin
cisplatin and tacrolimus both increase nephrotoxicity and/or ototoxicity. Use Caution/Monitor.
- citalopram
tacrolimus and citalopram both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor. ECG monitoring is recommended, along with drugs that may prolong the QT interval.
- clarithromycin
clarithromycin will increase the level or effect of tacrolimus by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor.
- clomipramine
tacrolimus and clomipramine both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
- clotrimazole
clotrimazole will decrease the level or effect of tacrolimus by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor.
- clozapine
clozapine and tacrolimus both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
- cobicistat
cobicistat will increase the level or effect of tacrolimus by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- colistin
colistin and tacrolimus both increase nephrotoxicity and/or ototoxicity. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- conivaptan
conivaptan will increase the level or effect of tacrolimus by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- conjugated estrogens
tacrolimus will increase the level or effect of conjugated estrogens by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor.
- conjugated estrogens, vaginal
tacrolimus will increase the level or effect of conjugated estrogens, vaginal by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor.
- cortisone
cortisone will decrease the level or effect of tacrolimus by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
tacrolimus will increase the level or effect of cortisone by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor. - crizotinib
crizotinib increases levels of tacrolimus by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor.
- crofelemer
crofelemer increases levels of tacrolimus by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Crofelemer has the potential to inhibit CYP3A4 at concentrations expected in the gut; unlikely to inhibit systemically because minimally absorbed.
- dabigatran
tacrolimus will increase the level or effect of dabigatran by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor. Atrial fibrillation: Avoid coadministering dabigatran with P-gp inhibitors if CrCl <30 mL/min. DVT/PE treatment: Avoid coadministering dabigatran with P-gp inhibitors if CrCl <50 mL/min
- danicopan
danicopan will increase the level or effect of tacrolimus by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor. Danicopan increases plasma concentrations of P-gp substrates; consider dose reduction of P-gp substrates where minimal concentration changes may lead to serious adverse reactions.
- darifenacin
darifenacin will increase the level or effect of tacrolimus by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- darunavir
darunavir will increase the level or effect of tacrolimus by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- dasatinib
dasatinib will increase the level or effect of tacrolimus by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
dasatinib and tacrolimus both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor. - daunorubicin
tacrolimus will increase the level or effect of daunorubicin by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor.
- deferasirox
deferasirox will decrease the level or effect of tacrolimus by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Coadministration of deferasirox with potentially nephrotoxic drugs, including tacrolimus, may increase the risk of this toxicity. Monitor serum creatinine and/or creatinine clearance in patients.
- deflazacort
tacrolimus will increase the level or effect of deflazacort by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor.
- degarelix
degarelix and tacrolimus both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
- dengue vaccine
tacrolimus decreases effects of dengue vaccine by immunosuppressive effects; risk of infection. Use Caution/Monitor. Immunosuppressive therapies (eg, irradiation, antimetabolites, alkylating agents, cytotoxic drugs, corticosteroids [greater than physiologic doses]) may reduce immune response to dengue vaccine.
- denosumab
tacrolimus, denosumab. Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor. Comment: Caution should be taken in patients on concomitant immunosuppressants or with impaired immune systems because of increased risk for serious infections.
- desipramine
desipramine and tacrolimus both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
- deutetrabenazine
deutetrabenazine and tacrolimus both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor. At the maximum recommended dose, deutetrabenazine does not prolong QT interval to a clinically relevant extent. Certain circumstances may increase risk of torsade de pointes and/or sudden death in association with drugs that prolong the QTc interval (eg, bradycardia, hypokalemia or hypomagnesemia, coadministration with other drugs that prolong QTc interval, presence of congenital QT prolongation).
- dexamethasone
dexamethasone will decrease the level or effect of tacrolimus by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
tacrolimus will increase the level or effect of dexamethasone by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor. - dexlansoprazole
dexlansoprazole will increase the level or effect of tacrolimus by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2C19 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Dexlansoprazole and tacrolimus compete for CYP2C19 metabolism. Concomitant administration may increase tacrolimus whole blood concentrations, particularly in intermediate or poor metabolizers of CYP2C19
- DHEA, herbal
DHEA, herbal will increase the level or effect of tacrolimus by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- dichlorphenamide
dichlorphenamide and tacrolimus both decrease serum potassium. Use Caution/Monitor.
dichlorphenamide, tacrolimus. Either increases toxicity of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Both drugs can cause metabolic acidosis. - digoxin
tacrolimus will increase the level or effect of digoxin by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor.
- diltiazem
diltiazem will increase the level or effect of tacrolimus by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- docetaxel
tacrolimus will increase the level or effect of docetaxel by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor.
- dofetilide
dofetilide increases toxicity of tacrolimus by QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
- dolasetron
dolasetron and tacrolimus both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
- donepezil
donepezil and tacrolimus both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
- doxepin
doxepin and tacrolimus both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
- doxorubicin
tacrolimus will increase the level or effect of doxorubicin by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor.
- doxorubicin liposomal
tacrolimus will increase the level or effect of doxorubicin liposomal by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor.
- dronabinol
dronabinol increases levels of tacrolimus by plasma protein binding competition. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Dronabinol is highly bound to plasma proteins and may displace and increase the free fraction of other concomitantly administered highly protein-bound drugs. This has not been confirmed in vivo. Caution with narrow therapeutic index drugs that are highly protein bound when initiating or increasing the dose of dronabinol.
- dronedarone
dronedarone will increase the level or effect of tacrolimus by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- dulaglutide
dulaglutide, tacrolimus. Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor. Comment: Dulaglutide slows gastric emptying and may impact absorption of concomitantly administered oral medications; be particularly cautious when coadministered with drugs that have a narrow therapeutic index.
- dupilumab
dupilumab, tacrolimus. Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor. Comment: Formation of CYP450 enzymes can be altered by increased levels of certain cytokines during chronic inflammation; thus, dupilumab could normalize the formation of CYP450 enzymes. Upon initiation or discontinuation of dupilumab in patients who are receiving concomitant CYP450 substrates, particularly those with a narrow therapeutic index, consider monitoring for therapeutic effect.
- duvelisib
duvelisib will increase the level or effect of tacrolimus by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Coadministration with duvelisib increases AUC of a sensitive CYP3A4 substrate which may increase the risk of toxicities of these drugs. Consider reducing the dose of the sensitive CYP3A4 substrate and monitor for signs of toxicities of the coadministered sensitive CYP3A substrate.
- echinacea
tacrolimus increases and echinacea decreases immunosuppressive effects; risk of infection. Effect of interaction is not clear, use caution. Use Caution/Monitor.
- efavirenz
efavirenz and tacrolimus both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
- elacestrant
elacestrant will increase the level or effect of tacrolimus by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Reduce dose of P-gp substrates per their Prescribing Information when minimal concentration changes may lead to serious or life-threatening adverse reactions.
- elagolix
elagolix will increase the level or effect of tacrolimus by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor.
elagolix decreases levels of tacrolimus by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Elagolix is a weak-to-moderate CYP3A4 inducer. Monitor CYP3A substrates if coadministered. Consider increasing CYP3A substrate dose if needed. - elbasvir/grazoprevir
elbasvir/grazoprevir increases levels of tacrolimus by unknown mechanism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Frequently monitor tacrolimus whole blood concentrations, renal function, and tacrolimus-associated adverse events if coadministered with elbasvir/grazoprevir.
- eliglustat
eliglustat increases levels of tacrolimus by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Monitor therapeutic drug concentrations, as indicated, or consider reducing the dosage of the P-gp substrate and titrate to clinical effect.
tacrolimus and eliglustat both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor. - elranatamab
elranatamab will increase the level or effect of tacrolimus by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Elranatamab causes cytokine release syndrome (CRS) that may suppress activity of CYP enzymes, resulting in increased exposure of CYP substrates. This is more likely to occur from initiation of elranatamab step-up dosing up to 14 days after the first treatment dose and during and after CRS.
- eluxadoline
eluxadoline increases levels of tacrolimus by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Caution when CYP3A substrates that have a narrow therapeutic index are coadministered with eluxadoline.
- elvitegravir/cobicistat/emtricitabine/tenofovir DF
elvitegravir/cobicistat/emtricitabine/tenofovir DF increases levels of tacrolimus by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Cobicistat is a CYP3A4 inhibitor; contraindicated with CYP3A4 substrates for which elevated plasma concentrations are associated with serious and/or life-threatening events.
tacrolimus and elvitegravir/cobicistat/emtricitabine/tenofovir DF both increase nephrotoxicity and/or ototoxicity. Use Caution/Monitor. - encorafenib
encorafenib, tacrolimus. affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Encorafenib both inhibits and induces CYP3A4 at clinically relevant plasma concentrations. Coadministration of encorafenib with sensitive CYP3A4 substrates may result in increased toxicity or decreased efficacy of these agents.
- epcoritamab
epcoritamab, tacrolimus. affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Epcoritamab causes release of cytokines that may suppress activity of CYP enzymes, resulting in increased exposure of CYP substrates. For certain CYP substrates, minimal changes in their concentration may lead to serious adverse reactions. If needed, modify therapy as recommended in the substrate's prescribing information. .
- erythromycin base
erythromycin base will increase the level or effect of tacrolimus by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor.
- erythromycin ethylsuccinate
erythromycin ethylsuccinate will increase the level or effect of tacrolimus by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor.
- erythromycin lactobionate
erythromycin lactobionate will increase the level or effect of tacrolimus by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor.
- erythromycin stearate
erythromycin stearate will increase the level or effect of tacrolimus by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor.
- escitalopram
escitalopram increases toxicity of tacrolimus by QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
- eslicarbazepine acetate
eslicarbazepine acetate will decrease the level or effect of tacrolimus by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- esomeprazole
esomeprazole will increase the level or effect of tacrolimus by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2C19 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Concomitant administration may increase tacrolimus whole blood concentrations, particularly in intermediate or poor metabolizers of CYP2C19
- estradiol
tacrolimus will increase the level or effect of estradiol by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor.
- estrogens conjugated synthetic
tacrolimus will increase the level or effect of estrogens conjugated synthetic by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor.
- estrogens esterified
tacrolimus will increase the level or effect of estrogens esterified by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor.
- estropipate
tacrolimus will increase the level or effect of estropipate by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor.
- ethinylestradiol
ethinylestradiol will increase the level or effect of tacrolimus by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- etoposide
tacrolimus will increase the level or effect of etoposide by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor.
- etravirine
etravirine will decrease the level or effect of tacrolimus by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- everolimus
tacrolimus and everolimus both increase nephrotoxicity and/or ototoxicity. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. If used for liver transplant immunosuppression (Zortress), reduce tacrolimus dose and use target serum concentration to reduce nephrotoxicity.
- ezogabine
ezogabine, tacrolimus. Either increases toxicity of the other by QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor. Slight and transient QT-prolongation observed with ezogabine, particularly when dose titrated to 1200 mg/day. QT interval should be monitored when ezogabine is prescribed with agents known to increase QT interval.
- fedratinib
fedratinib will increase the level or effect of tacrolimus by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Adjust dose of drugs that are CYP3A4 substrates as necessary.
- felodipine
felodipine will increase the level or effect of tacrolimus by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor.
- ferric maltol
ferric maltol, tacrolimus. Either increases levels of the other by unspecified interaction mechanism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Coadministration of ferric maltol with certain oral medications may decrease the bioavailability of either ferric maltol and some oral drugs. For oral drugs where reductions in bioavailability may cause clinically significant effects on its safety or efficacy, separate administration of ferric maltol from these drugs. Duration of separation may depend on the absorption of the medication concomitantly administered (eg, time to peak concentration, whether the drug is an immediate or extended release product).
- finerenone
tacrolimus will increase the level or effect of finerenone by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Monitor serum potassium during initiation and dosage adjustment of either finererone or weak CYP3A4 inhibitors. Adjust finererone dosage as needed.
tacrolimus and finerenone both increase serum potassium. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Finerenone dose adjustment based on current serum potassium concentration. Monitor serum potassium and adjust finerenone dose as described in the prescribing information as necessary. - fingolimod
tacrolimus increases effects of fingolimod by immunosuppressive effects; risk of infection. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Concomitant therapy is expected to increase the risk of immunosuppression. Use caution when switching patients from long-acting therapies with immune effects. .
fingolimod and tacrolimus both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor. - flibanserin
tacrolimus will increase the level or effect of flibanserin by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Increased flibanserin adverse effects may occur if coadministered with multiple weak CYP3A4 inhibitors.
- fluconazole
fluconazole will increase the level or effect of tacrolimus by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- fludrocortisone
fludrocortisone will decrease the level or effect of tacrolimus by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
tacrolimus will increase the level or effect of fludrocortisone by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor. - fluoxetine
tacrolimus and fluoxetine both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
- fluphenazine
tacrolimus and fluphenazine both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
- fluvastatin
tacrolimus increases toxicity of fluvastatin by Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor. Comment: OATP1B1 inhibitors may increase risk of myopathy.
- fluvoxamine
fluvoxamine will increase the level or effect of tacrolimus by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
tacrolimus and fluvoxamine both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor. - fosamprenavir
fosamprenavir will increase the level or effect of tacrolimus by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- fosaprepitant
fosaprepitant will increase the level or effect of tacrolimus by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- foscarnet
foscarnet and tacrolimus both increase nephrotoxicity and/or ototoxicity. Use Caution/Monitor.
- fosphenytoin
fosphenytoin will decrease the level or effect of tacrolimus by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
fosphenytoin will decrease the level or effect of tacrolimus by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor. - fostamatinib
fostamatinib will increase the level or effect of tacrolimus by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor. Concomitant use of fostamatinib may increase concentrations of P-gp substrates. Monitor for toxicities of the P-gp substrate drug that may require dosage reduction when given concurrently with fostamatinib.
- fostemsavir
tacrolimus and fostemsavir both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor. QTc prolongation reported with higher than recommended doses of fostemsavir.
- gemifloxacin
gemifloxacin and tacrolimus both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
- gemtuzumab
tacrolimus and gemtuzumab both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
- gentamicin
tacrolimus will increase the level or effect of gentamicin by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor.
gentamicin and tacrolimus both increase nephrotoxicity and/or ototoxicity. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. - gepirone
gepirone and tacrolimus both increase QTc interval. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- gilteritinib
gilteritinib and tacrolimus both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
- givinostat
tacrolimus and givinostat both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor. If coadministered, obtain ECGs when initiating, during concomitant use, and as clinically indicated. Withhold if QTc interval >500 ms or a change from baseline >60 ms.
givinostat will increase the level or effect of tacrolimus by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Givinostat is a weak CYP3A4 inhibitor. Closely monitor if coadministered with orally administered CYP3A4 sensitive substrates for which a small change in substrate plasma concentration may lead to serious toxicities. - glecaprevir/pibrentasvir
tacrolimus will increase the level or effect of glecaprevir/pibrentasvir by decreasing metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Caution when coadministering glecaprevir/pibrentasvir with OATP1B1/OATP1B3 inhibitors
glecaprevir/pibrentasvir will increase the level or effect of tacrolimus by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor. - glofitamab
glofitamab, tacrolimus. affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Glofitamab causes release of cytokines that may suppress activity of CYP enzymes, resulting in increased exposure of CYP substrates. For certain CYP substrates, minimal changes in their concentration may lead to serious adverse reactions. If needed, modify therapy as recommended in the substrate's prescribing information. .
- glycerol phenylbutyrate
glycerol phenylbutyrate will decrease the level or effect of tacrolimus by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Glycerol phenylbutyrate is a weak inducer of CYP3A4. Monitor for decreased efficacy of CYP3A4 substrates that have a narrow therapeutic index.
- goserelin
tacrolimus and goserelin both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
- granisetron
granisetron and tacrolimus both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
- grapefruit
grapefruit will increase the level or effect of tacrolimus by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- griseofulvin
griseofulvin will decrease the level or effect of tacrolimus by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- guselkumab
guselkumab, tacrolimus. Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor. Comment: Formation of CYP450 enzymes can be altered by increased levels of certain cytokines during chronic inflammation; thus, normalizing the formation of CYP450 enzymes. Upon initiation or discontinuation of guselkumab in patients who are receiving concomitant CYP450 substrates, particularly those with a narrow therapeutic index, consider monitoring for therapeutic effect.
- haemophilus influenzae type b vaccine
tacrolimus decreases effects of haemophilus influenzae type b vaccine by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Avoid vaccination during chemotherapy or radiation therapy if possible because antibody response might be suboptimal. Patients vaccinated within a 14-day period before starting or during immunosuppressive therapy should be revaccinated =3 months after therapy is discontinued if immune competence has been restored. .
- haloperidol
haloperidol and tacrolimus both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
- histrelin
tacrolimus and histrelin both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
- hydrocortisone
hydrocortisone will decrease the level or effect of tacrolimus by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
tacrolimus will increase the level or effect of hydrocortisone by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor. - hydroxyzine
hydroxyzine and tacrolimus both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
- ifosfamide
ifosfamide, tacrolimus. Either increases toxicity of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Ifosfamide may enhance the toxicities of myelosuppressive agents. Monitor for increased risk of myelosuppression.
- iloperidone
iloperidone increases levels of tacrolimus by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2E1 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Iloperidone is a time-dependent CYP3A inhibitor and may lead to increased plasma levels of drugs predominantly eliminated by CYP3A4.
- imatinib
tacrolimus will increase the level or effect of imatinib by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor.
- imipramine
tacrolimus and imipramine both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
- indacaterol, inhaled
indacaterol, inhaled, tacrolimus. QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor. Drugs that are known to prolong the QTc interval may have an increased the risk of ventricular arrhythmias.
- indinavir
indinavir will increase the level or effect of tacrolimus by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
indinavir will increase the level or effect of tacrolimus by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor. - influenza virus vaccine quadrivalent, recombinant
tacrolimus decreases effects of influenza virus vaccine quadrivalent, recombinant by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Use Caution/Monitor. Immune response to vaccine may be decreased in immunocompromised individuals.
- influenza virus vaccine trivalent, recombinant
tacrolimus decreases effects of influenza virus vaccine trivalent, recombinant by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Use Caution/Monitor. Immune response to vaccine may be decreased in immunocompromised individuals.
- irinotecan
tacrolimus will increase the level or effect of irinotecan by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor.
- irinotecan liposomal
tacrolimus will increase the level or effect of irinotecan liposomal by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor.
- isavuconazonium sulfate
tacrolimus will increase the level or effect of isavuconazonium sulfate by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
isavuconazonium sulfate will increase the level or effect of tacrolimus by Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor. Isavuconazonium sulfate, an inhibitor of P-gp and CYP3A4, may increase the effects or levels of sensitive P-gp or CYP3A4 substrates, which may require dose adjustment.
tacrolimus and isavuconazonium sulfate both decrease immunosuppressive effects; risk of infection. Use Caution/Monitor. - isoniazid
isoniazid will increase the level or effect of tacrolimus by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- istradefylline
istradefylline will increase the level or effect of tacrolimus by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Istradefylline 40 mg/day increased peak levels and AUC of CYP3A4 substrates in clinical trials. This effect was not observed with istradefylline 20 mg/day. Consider dose reduction of sensitive CYP3A4 substrates.
istradefylline will increase the level or effect of tacrolimus by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor. Istradefylline 40 mg/day increased peak levels and AUC of P-gp substrates in clinical trials. Consider dose reduction of sensitive P-gp substrates. - ivacaftor
ivacaftor increases levels of tacrolimus by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor. Ivacaftor and its M1 metabolite has the potential to inhibit P-gp; may significantly increase systemic exposure to sensitive P-gp substrates with a narrow therapeutic index.
- ivermectin
tacrolimus will increase the level or effect of ivermectin by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor.
- ixekizumab
ixekizumab, tacrolimus. Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor. Comment: Formation of CYP450 enzymes can be altered by increased levels of certain cytokines during chronic inflammation; thus, ixekizumab could normalize the formation of CYP450 enzymes. Upon initiation or discontinuation of ixekizumab in patients who are receiving concomitant CYP450 substrates, particularly those with a narrow therapeutic index, consider monitoring for therapeutic effect.
- ketoconazole
ketoconazole will increase the level or effect of tacrolimus by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor.
- lansoprazole
lansoprazole will increase the level or effect of tacrolimus by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2C19 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Concomitant administration may increase tacrolimus whole blood concentrations, particularly in intermediate or poor metabolizers of CYP2C19
- lapatinib
lapatinib will increase the level or effect of tacrolimus by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
lapatinib will increase the level or effect of tacrolimus by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor. - larotrectinib
larotrectinib will increase the level or effect of tacrolimus by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- lenacapavir
lenacapavir will increase the level or effect of tacrolimus by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Lencapavir may increase CYP3A4 substrates initiated within 9 months after last SC dose of lenacapavir, which may increase potential risk of adverse reactions of CYP3A4 substrates.
- letermovir
tacrolimus increases levels of letermovir by decreasing metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Coadminstration of letermovir, an OATP1B1/3 substrate, with OATP1B1/3 inhibitors may increase letermovir plasma concentrations.
letermovir increases levels of tacrolimus by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Monitor tacrolimus plasma concentrations during treatment and after discontinuation of letemovir and adjust dose of tacrolimus accordingly. - leuprolide
tacrolimus and leuprolide both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
- levamlodipine
levamlodipine will increase the level or effect of tacrolimus by unspecified interaction mechanism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Amlodipine may increase the systemic exposure of cyclosporine or tacrolimus when coadministered. Frequent monitoring of trough blood levels of cyclosporine and tacrolimus is recommended and adjust the dose when appropriate.
- levofloxacin
tacrolimus and levofloxacin both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
- levoketoconazole
levoketoconazole will increase the level or effect of tacrolimus by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor.
- lithium
lithium and tacrolimus both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
- lomitapide
lomitapide increases levels of tacrolimus by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Consider reducing dose when used concomitantly with lomitapide.
- lomustine
lomustine and tacrolimus both increase immunosuppressive effects; risk of infection. Use Caution/Monitor. Concomitant therapy is expected to increase the risk of immunosuppression. Use caution when switching patients from long-acting therapies with immune effects.
- lonafarnib
lonafarnib will increase the level or effect of tacrolimus by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Lonafarnib is a weak P-gp inhibitor. Monitor for adverse reactions if coadministered with P-gp substrates where minimal concentration changes may lead to serious or life-threatening toxicities. Reduce P-gp substrate dose if needed.
- lonapegsomatropin
lonapegsomatropin will decrease the level or effect of tacrolimus by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Limited published data indicate that growth hormone treatment increases cytochrome P450 (CYP450)-mediated antipyrine clearance. Caution with sensitive CYP substrates
- loperamide
tacrolimus will increase the level or effect of loperamide by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor.
tacrolimus and loperamide both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor. - loratadine
loratadine will increase the level or effect of tacrolimus by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor.
- lovastatin
lovastatin will increase the level or effect of tacrolimus by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor.
- lumefantrine
lumefantrine will decrease the level or effect of tacrolimus by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- maitake
tacrolimus increases and maitake decreases immunosuppressive effects; risk of infection. Effect of interaction is not clear, use caution. Use Caution/Monitor.
- maprotiline
tacrolimus and maprotiline both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
- maraviroc
tacrolimus will increase the level or effect of maraviroc by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor.
- marijuana
marijuana will increase the level or effect of tacrolimus by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- meningococcal group B vaccine
tacrolimus decreases effects of meningococcal group B vaccine by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Use Caution/Monitor. Individuals with altered immunocompetence may have reduced immune responses to the vaccine.
- mercaptopurine
mercaptopurine and tacrolimus both increase immunosuppressive effects; risk of infection. Use Caution/Monitor.
- mestranol
tacrolimus will increase the level or effect of mestranol by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor.
- metformin
tacrolimus decreases effects of metformin by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- methotrexate
methotrexate and tacrolimus both increase immunosuppressive effects; risk of infection. Use Caution/Monitor. Combination may increase risk of myelosuppression.
- methoxyflurane
methoxyflurane and tacrolimus both increase nephrotoxicity and/or ototoxicity. Use Caution/Monitor.
- methylprednisolone
methylprednisolone will decrease the level or effect of tacrolimus by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
tacrolimus will increase the level or effect of methylprednisolone by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor. - methyltestosterone
methyltestosterone increases effects of tacrolimus by decreasing metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- metoclopramide intranasal
metoclopramide intranasal will increase the level or effect of tacrolimus by Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor. Metoclopramide may increase the absorption of tacrolimus. Monitor therapeutic drug concentrations and adjust the dose as needed.
- metronidazole
metronidazole will increase the level or effect of tacrolimus by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- miconazole vaginal
miconazole vaginal will increase the level or effect of tacrolimus by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- mirtazapine
mirtazapine and tacrolimus both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
- mitotane
mitotane decreases levels of tacrolimus by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Mitotane is a strong inducer of cytochrome P-4503A4; monitor when coadministered with CYP3A4 substrates for possible dosage adjustments.
- momelotinib
tacrolimus increases toxicity of momelotinib by Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor. Comment: OATP1B1/B3 inhibitor increases momelotinib (OATP1B1/B3 subtrate) plasma concentrations, which may increase the risk of adverse reactions with momelotinib.
- nafcillin
nafcillin will decrease the level or effect of tacrolimus by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- naldemedine
tacrolimus increases levels of naldemedine by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor. Monitor naldemedine for potential adverse effects if coadministered with P-gp inhibitors.
- nefazodone
nefazodone will increase the level or effect of tacrolimus by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor.
- nelfinavir
nelfinavir will increase the level or effect of tacrolimus by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
tacrolimus will increase the level or effect of nelfinavir by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor. - neomycin PO
tacrolimus will increase the level or effect of neomycin PO by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor.
- nevirapine
nevirapine will decrease the level or effect of tacrolimus by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- nicardipine
nicardipine will increase the level or effect of tacrolimus by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor.
nicardipine increases levels of tacrolimus by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. - nifedipine
nifedipine will increase the level or effect of tacrolimus by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
nifedipine will decrease the level or effect of tacrolimus by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor. - nilotinib
nilotinib will increase the level or effect of tacrolimus by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
nilotinib will increase the level or effect of tacrolimus by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor. - nintedanib
tacrolimus increases levels of nintedanib by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. If nintedanib adverse effects occur, management may require interruption, dose reduction, or discontinuation of therapy .
- nitazoxanide
nitazoxanide, tacrolimus. Either increases levels of the other by Mechanism: plasma protein binding competition. Use Caution/Monitor.
- nortriptyline
tacrolimus and nortriptyline both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
- ocrelizumab
tacrolimus and ocrelizumab both increase immunosuppressive effects; risk of infection. Use Caution/Monitor. Coadministration of ocrelizumab with immunosuppressants may increase the risk of immunosuppression.
- octreotide
tacrolimus and octreotide both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
- ofatumumab SC
ofatumumab SC, tacrolimus. Either increases effects of the other by immunosuppressive effects; risk of infection. Use Caution/Monitor. Consider the risk of additive immune system effects when coadministering immunosuppressive therapies with coadministration. When switching from therapies with immune effects, take into account the duration and mechanism of action of these therapies when initiating ofatumumab SC.
- ofloxacin
tacrolimus and ofloxacin both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
- olanzapine
olanzapine and tacrolimus both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
- olaparib
tacrolimus and olaparib both increase pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Coadministration with other other myelosuppressive anticancer agents, including DNA damaging agents, may potentiate and prolongate the myelosuppressive toxicity.
- olodaterol inhaled
tacrolimus and olodaterol inhaled both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor. Drugs that prolong the QTc interval and may potentiate the effects of beta2 agonists on the cardiovascular system; increased risk of ventricular arrhythmias
- omaveloxolone
omaveloxolone will decrease the level or effect of tacrolimus by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Omaveloxolone may reduce systemic exposure of sensitive CYP3A4 substrates. Check prescribing information of substrate if dosage modification is needed.
- ombitasvir/paritaprevir/ritonavir & dasabuvir (DSC)
ombitasvir/paritaprevir/ritonavir & dasabuvir (DSC) will increase the level or effect of tacrolimus by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. When initiating therapy with Viekira Pak, the dose of tacrolimus needs to be reduced; do not administer tacrolimus on the day Viekira Pak is initiated; beginning the day after Viekira Pak is initiated, reinitiate tacrolimus at a reduced dose based on tacrolimus blood concentrations; typical tacrolimus dosing is 0.5 mg q7days; measure tacrolimus blood concentrations and adjust dose or dosing frequency to determine subsequent dose modifications; upon completion of Viekira Pak, the appropriate time to resume pre-Viekira Pak dose of tacrolimus should be guided by assessment of blood concentrations
- omeprazole
omeprazole will increase the level or effect of tacrolimus by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2C19 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Concomitant administration may increase tacrolimus whole blood concentrations, particularly in intermediate or poor metabolizers of CYP2C19
- oritavancin
oritavancin will decrease the level or effect of tacrolimus by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Oritavancin is a weak CYP3A4 inducer; caution if coadministered with CYP3A4 substrates that have a narrow therapeutic index
- osilodrostat
osilodrostat and tacrolimus both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
- osimertinib
osimertinib and tacrolimus both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor. Conduct periodic monitoring with ECGs and electrolytes in patients taking drugs known to prolong the QTc interval.
- ospemifene
tacrolimus, ospemifene. Either increases levels of the other by plasma protein binding competition. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- oxaliplatin
oxaliplatin and tacrolimus both increase nephrotoxicity and/or ototoxicity. Use Caution/Monitor.
- oxcarbazepine
oxcarbazepine will decrease the level or effect of tacrolimus by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- ozanimod
ozanimod and tacrolimus both increase QTc interval. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. The potential additive effects on heart rate, treatment with ozanimod should generally not be initiated in patients who are concurrently treated with QT prolonging drugs with known arrhythmogenic properties.
ozanimod, tacrolimus. Either increases effects of the other by immunosuppressive effects; risk of infection. Use Caution/Monitor. Coadministration with immunosuppressive therapies may increase the risk of additive immune effects during therapy and in the weeks following administration. When switching from drugs with prolonged immune effects, consider the half-life and mode of action of these drugs in order to avoid unintended additive immunosuppressive effects. - paclitaxel
tacrolimus will increase the level or effect of paclitaxel by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor.
- paclitaxel protein bound
tacrolimus will increase the level or effect of paclitaxel protein bound by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor.
- palbociclib
palbociclib will increase the level or effect of tacrolimus by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. The dose of sensitive CYP3A substrates with a narrow therapeutic index may need to be reduced if coadministered with palbociclib
- paliperidone
tacrolimus will increase the level or effect of paliperidone by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor.
- pantoprazole
pantoprazole will increase the level or effect of tacrolimus by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2C19 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Concomitant administration may increase tacrolimus whole blood concentrations, particularly in intermediate or poor metabolizers of CYP2C19
- paromomycin
tacrolimus will increase the level or effect of paromomycin by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor.
paromomycin and tacrolimus both increase nephrotoxicity and/or ototoxicity. Use Caution/Monitor. - pentamidine
pentamidine and tacrolimus both increase nephrotoxicity and/or ototoxicity. Use Caution/Monitor.
- pentobarbital
pentobarbital will decrease the level or effect of tacrolimus by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- peramivir
tacrolimus increases levels of peramivir by decreasing renal clearance. Use Caution/Monitor. Caution when peramivir coadministered with nephrotoxic drugs.
- perphenazine
tacrolimus and perphenazine both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
- phenobarbital
phenobarbital will decrease the level or effect of tacrolimus by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
phenobarbital will decrease the level or effect of tacrolimus by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor. - phenytoin
phenytoin will decrease the level or effect of tacrolimus by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
phenytoin will decrease the level or effect of tacrolimus by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor. Tacrolimus dosage requirements may be greater when administered concurrently with phenytoin. - pirtobrutinib
pirtobrutinib will increase the level or effect of tacrolimus by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Pirtobrutinib (a CYP3A4 inhibitor) may increase plasma concentrations of sensitive CYP3A4 substrate which may increase the risk of adverse reactions related to these substrates.
- pitavastatin
tacrolimus increases toxicity of pitavastatin by Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor. Comment: OATP1B1 inhibitors may increase risk of myopathy.
- pitolisant
pitolisant will decrease the level or effect of tacrolimus by Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor. Pitolisant is a borderline/weak inducer of CYP3A4. Monitor sensitive CYP3A4 substrates for reduced effectiveness if coadministered.
- poliovirus vaccine inactivated
tacrolimus decreases effects of poliovirus vaccine inactivated by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Avoid vaccination during chemotherapy or radiation therapy if possible because antibody response might be suboptimal. Patients vaccinated within a 14-day period before starting or during immunosuppressive therapy should be revaccinated =3 months after therapy is discontinued if immune competence has been restored. .
- polymyxin B
polymyxin B and tacrolimus both increase nephrotoxicity and/or ototoxicity. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- ponatinib
ponatinib increases levels of tacrolimus by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor.
- ponesimod
ponesimod and tacrolimus both increase immunosuppressive effects; risk of infection. Use Caution/Monitor. Caution if coadministered because of additive immunosuppressive effects during such therapy and in the weeks following administration. When switching from drugs with prolonged immune effects, consider the half-life and mode of action of these drugs to avoid unintended additive immunosuppressive effects.
- posaconazole
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of tacrolimus by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
tacrolimus will increase the level or effect of posaconazole by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor. - potassium citrate
tacrolimus and potassium citrate both increase serum potassium. Use Caution/Monitor.
- potassium citrate/citric acid
tacrolimus and potassium citrate/citric acid both increase serum potassium. Use Caution/Monitor.
- pravastatin
tacrolimus increases toxicity of pravastatin by Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor. Comment: OATP1B1 inhibitors may increase risk of myopathy.
- prednisolone
tacrolimus will increase the level or effect of prednisolone by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor.
- prednisone
prednisone will decrease the level or effect of tacrolimus by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
tacrolimus will increase the level or effect of prednisone by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor. - primaquine
primaquine and tacrolimus both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
- primidone
primidone will decrease the level or effect of tacrolimus by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- prochlorperazine
tacrolimus and prochlorperazine both decrease QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
- promethazine
tacrolimus and promethazine both decrease QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
- quercetin
quercetin will decrease the level or effect of tacrolimus by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor.
- quetiapine
quetiapine, tacrolimus. Either increases toxicity of the other by QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor. Avoid use with drugs that prolong QT and in patients with risk factors for prolonged QT interval. Postmarketing cases show QT prolongation with overdose in patients with concomitant illness or with drugs known to cause electrolyte imbalance or prolong QT.
- quinine
tacrolimus and quinine both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
- quinupristin/dalfopristin
quinupristin/dalfopristin will increase the level or effect of tacrolimus by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- quizartinib
quizartinib, tacrolimus. Either increases effects of the other by QTc interval. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Monitor patients more frequently with ECG if coadministered with QT prolonging drugs.
- rabeprazole
rabeprazole will increase the level or effect of tacrolimus by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2C19 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Concomitant administration may increase tacrolimus whole blood concentrations, particularly in intermediate or poor metabolizers of CYP2C19
rabeprazole, tacrolimus. Either increases toxicity of the other by Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor. Comment: Contomitant use of agents that can cause magnesium loss can result in hypomagnesemia. - ranolazine
ranolazine will increase the level or effect of tacrolimus by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor.
- ribociclib
ribociclib will increase the level or effect of tacrolimus by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Caution if ribociclib is coadministered with sensitive CYP3A4 substrates that have a narrow therapeutic index. Dose reduction for sensitive CYP3A4 substrates may be needed.
- rifampin
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of tacrolimus by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor.
- rifapentine
rifapentine will decrease the level or effect of tacrolimus by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- rifaximin
tacrolimus increases levels of rifaximin by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor.
- rilpivirine
rilpivirine increases toxicity of tacrolimus by QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor. Rilpivirine should be used with caution when co-administered with a drug with a known risk of Torsade de Pointes.
- risperidone
tacrolimus will increase the level or effect of risperidone by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor.
tacrolimus and risperidone both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor. - ritlecitinib
ritlecitinib will increase the level or effect of tacrolimus by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Ritlecitinib inhibits CYP3A4 substrates; coadministration increases AUC and peak plasma concentration sensitive substrates, which may increase risk of adverse reactions. Additional monitoring and dosage adjustment may be needed in accordance with product labeling of CYP3A substrates.
- ritonavir
ritonavir will increase the level or effect of tacrolimus by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
ritonavir will increase the level or effect of tacrolimus by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor. - romidepsin
tacrolimus will increase the level or effect of romidepsin by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor.
- roxithromycin
roxithromycin increases levels of tacrolimus by decreasing metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- rucaparib
rucaparib will increase the level or effect of tacrolimus by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Adjust dosage of CYP3A4 substrates, if clinically indicated.
- rufinamide
rufinamide will decrease the level or effect of tacrolimus by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- sacubitril/valsartan
tacrolimus will increase the level or effect of sacubitril/valsartan by Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor. The results from an in vitro study with human liver tissue indicate that valsartan is a substrate of the hepatic uptake transporter OATP1B1; coadministration with OATP1B1 inhibitors may increase valsartan systemic exposure
- saquinavir
tacrolimus will increase the level or effect of saquinavir by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor.
- sarecycline
sarecycline will increase the level or effect of tacrolimus by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor. Monitor for toxicities of P-gp substrates that may require dosage reduction when coadministered with P-gp inhibitors.
- sarilumab
sarilumab, tacrolimus. Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor. Comment: Formation of CYP450 enzymes can be altered by increased levels of cytokines such as IL-6. Elevated IL-6 concentration may down-regulate CYP activity, such as in patients with RA, and, hence, increase drug levels compared with subjects without RA. Blockade of IL-6 signaling by IL-6 antagonists (eg, sarilumab) might reverse the inhibitory effect of IL-6 and restore CYP activity, leading to decreased drug concentrations. Caution when initiating or discontinuing sarilumab if coadministered with CYP450 substrates, especially those with a narrow therapeutic index.
- schisandra
schisandra will increase the level or effect of tacrolimus by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- secobarbital
secobarbital will decrease the level or effect of tacrolimus by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- secukinumab
secukinumab, tacrolimus. Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor. Comment: Formation of CYP450 enzymes can be altered by increased levels of certain cytokines during chronic inflammation; thus, secukinumab could normalize the formation of CYP450 enzymes. Upon initiation or discontinuation of secukinumab in patients who are receiving concomitant CYP450 substrates, particularly those with a narrow therapeutic index, consider monitoring for therapeutic effect.
- selpercatinib
selpercatinib increases toxicity of tacrolimus by QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
- sertraline
sertraline and tacrolimus both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
- silodosin
tacrolimus will increase the level or effect of silodosin by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor.
- siltuximab
siltuximab, tacrolimus. Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor. Comment: CYP450 activity in the liver is down regulated by infection and inflammation stimuli including cytokines (eg, IL-6); inhibition of IL-6 by siltuximab may restore CYP450 enzymatic activity; caution if coadministered with CYP substrates that have a narrow therapeutic index.
- simvastatin
simvastatin will increase the level or effect of tacrolimus by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor.
tacrolimus increases toxicity of simvastatin by Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor. Comment: OATP1B1 inhibitors may increase risk of myopathy. - siponimod
siponimod and tacrolimus both increase immunosuppressive effects; risk of infection. Use Caution/Monitor. Caution if coadministered because of additive immunosuppressive effects during such therapy and in the weeks following administration. When switching from drugs with prolonged immune effects, consider the half-life and mode of action of these drugs to avoid unintended additive immunosuppressive effects.
- sipuleucel-T
tacrolimus decreases effects of sipuleucel-T by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- sirolimus
sirolimus will increase the level or effect of tacrolimus by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor.
- solifenacin
solifenacin and tacrolimus both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
tacrolimus and solifenacin both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor. - somapacitan
somapacitan will decrease the level or effect of tacrolimus by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Limited published data indicate that growth hormone treatment increases cytochrome P450 (CYP450)-mediated antipyrine clearance. Caution with sensitive CYP substrates
- somatrogon
somatrogon will decrease the level or effect of tacrolimus by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Limited published data indicate that growth hormone treatment increases cytochrome P450 (CYP450)-mediated antipyrine clearance. Caution with sensitive CYP substrates
- somatropin
somatropin will decrease the level or effect of tacrolimus by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Limited published data indicate that growth hormone treatment increases cytochrome P450 (CYP450)-mediated antipyrine clearance. Caution with sensitive CYP substrates
- sorafenib
sorafenib and tacrolimus both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
- spironolactone
spironolactone will increase the level or effect of tacrolimus by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. tacrolimus dose may need to be adjusted
- St John's Wort
St John's Wort will decrease the level or effect of tacrolimus by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor.
- stiripentol
stiripentol, tacrolimus. affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Stiripentol is a CYP3A4 inhibitor and inducer. Monitor CYP3A4 substrates coadministered with stiripentol for increased or decreased effects. CYP3A4 substrates may require dosage adjustment.
stiripentol will increase the level or effect of tacrolimus by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Consider reducing the dose of P-glycoprotein (P-gp) substrates, if adverse reactions are experienced when administered concomitantly with stiripentol. - streptomycin
tacrolimus will increase the level or effect of streptomycin by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor.
streptomycin and tacrolimus both increase nephrotoxicity and/or ototoxicity. Use Caution/Monitor. - streptozocin
streptozocin and tacrolimus both increase nephrotoxicity and/or ototoxicity. Use Caution/Monitor.
- sunitinib
sunitinib and tacrolimus both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
tacrolimus and sunitinib both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor. - talquetamab
talquetamab will increase the level or effect of tacrolimus by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Talquetamab causes cytokine release syndrome (CRS) that may suppress activity of CYP enzymes, resulting in increased exposure of CYP substrates. This is more likely to occur from initiation of talquetamab step-up dosing up to 14 days after the first treatment dose and during and after CRS.
- tazemetostat
tazemetostat will decrease the level or effect of tacrolimus by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
tacrolimus will increase the level or effect of tazemetostat by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. - teclistamab
teclistamab will increase the level or effect of tacrolimus by altering metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Teclistamab causes release of cytokines that may suppress activity of CYP450 enzymes, resulting in increased exposure of CYP substrates. Monitor for increased concentrations or toxicities of sensitive CYP substrates. Adjust dose of CYP substrate drug as needed.
- tecovirimat
tecovirimat will decrease the level or effect of tacrolimus by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Tecovirimat is a weak CYP3A4 inducer. Monitor sensitive CYP3A4 substrates for effectiveness if coadministered.
- teduglutide
teduglutide increases levels of tacrolimus by Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor. Comment: Teduglutide may increase absorption of concomitant PO medications; caution with with drugs requiring titration or those with a narrow therapeutic index; dose adjustment may be necessary.
- telotristat ethyl
telotristat ethyl will decrease the level or effect of tacrolimus by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Telotristat ethyl induces CYP3A4 and may reduce systemic exposure of sensitive CYP3A4 substrates. Monitor for suboptimal efficacy and consider increasing the dose of the CYP3A4 substrate.
- teniposide
tacrolimus will increase the level or effect of teniposide by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor.
- tenofovir DF
tacrolimus and tenofovir DF both increase nephrotoxicity and/or ototoxicity. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- tinidazole
tinidazole will increase the level or effect of tacrolimus by unknown mechanism. Use Caution/Monitor. Monitored for signs of calcineurin-inhibitor associated toxicities (eg, nephrotoxicity, cholestasis, paresthesias).
tacrolimus will increase the level or effect of tinidazole by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. - tipranavir
tipranavir, tacrolimus. Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor. Comment: Tacrolimus levels may incr or decr, due to contradictory effects of tipranavir on hepatic CYP3A4 and P glycoprotein.
- tobramycin
tacrolimus will increase the level or effect of tobramycin by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor.
tacrolimus and tobramycin both increase nephrotoxicity and/or ototoxicity. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. - tolvaptan
tacrolimus will increase the level or effect of tolvaptan by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor.
tolvaptan will increase the level or effect of tacrolimus by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor. - topiramate
topiramate will decrease the level or effect of tacrolimus by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- trastuzumab
trastuzumab, tacrolimus. Either increases toxicity of the other by immunosuppressive effects; risk of infection. Use Caution/Monitor. Neutropenia or febrile neutropenia incidence were increased when trastuzumab was coadministered with myelosuppressive chemotherapy.
- trastuzumab deruxtecan
trastuzumab deruxtecan, tacrolimus. Either increases toxicity of the other by immunosuppressive effects; risk of infection. Use Caution/Monitor. Neutropenia or febrile neutropenia incidence were increased when trastuzumab was coadministered with myelosuppressive chemotherapy.
- trazodone
trazodone will decrease the level or effect of tacrolimus by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor.
- triclabendazole
tacrolimus and triclabendazole both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
- trifluoperazine
tacrolimus and trifluoperazine both decrease QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
- trimipramine
tacrolimus and trimipramine both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
- triptorelin
tacrolimus and triptorelin both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
- trofinetide
trofinetide will increase the level or effect of tacrolimus by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Monitor CYP3A4 substrates for which a small increase in plasma concentration may lead to serious toxicities if coadministered with trofinetide (a weak CYP3A4 inhibitor).
- tucatinib
tucatinib will increase the level or effect of tacrolimus by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor. Consider reducing the dosage of P-gp substrates, where minimal concentration changes may lead to serious or life-threatening toxicities.
- turmeric
turmeric will increase the level or effect of tacrolimus by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- ublituximab
ublituximab and tacrolimus both increase immunosuppressive effects; risk of infection. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Owing to potential additive immunosuppressive effects, consider duration of effect and mechanism of action of these therapies if coadministered
- ustekinumab
ustekinumab, tacrolimus. Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor. Comment: Formation of CYP450 enzymes can be altered by increased levels of certain cytokines during chronic inflammation; thus, normalizing the formation of CYP450 enzymes. Upon initiation or discontinuation of ustekinumab in patients who are receiving concomitant CYP450 substrates, particularly those with a narrow therapeutic index, consider monitoring for therapeutic effect.
- valbenazine
valbenazine and tacrolimus both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
- vancomycin
tacrolimus and vancomycin both increase nephrotoxicity and/or ototoxicity. Use Caution/Monitor.
- vardenafil
tacrolimus and vardenafil both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
- venlafaxine
tacrolimus and venlafaxine both decrease QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
- verapamil
verapamil will increase the level or effect of tacrolimus by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
verapamil will increase the level or effect of tacrolimus by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor. - vinblastine
tacrolimus will increase the level or effect of vinblastine by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor.
- vincristine
tacrolimus will increase the level or effect of vincristine by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor.
- vincristine liposomal
tacrolimus will increase the level or effect of vincristine liposomal by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor.
- voclosporin
voclosporin and tacrolimus both increase serum potassium. Use Caution/Monitor.
voclosporin, tacrolimus. Either increases effects of the other by QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor. - vonoprazan
vonoprazan will increase the level or effect of tacrolimus by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Vonoprazan is weak CYP3A inhibitor. Caution with sensitive CYP3A substrates.
- voriconazole
voriconazole will increase the level or effect of tacrolimus by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- vorinostat
tacrolimus and vorinostat both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
vorinostat and tacrolimus both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor. - zafirlukast
zafirlukast will increase the level or effect of tacrolimus by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- zoster vaccine recombinant
tacrolimus decreases effects of zoster vaccine recombinant by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Use Caution/Monitor. Immunosuppressive therapies may reduce the effectiveness of zoster vaccine recombinant.
Minor (42)
- acetazolamide
acetazolamide will increase the level or effect of tacrolimus by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- aliskiren
tacrolimus will increase the level or effect of aliskiren by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- allopurinol
allopurinol increases levels of tacrolimus by unknown mechanism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- alvimopan
tacrolimus will increase the level or effect of alvimopan by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- amiodarone
amiodarone increases levels of tacrolimus by decreasing renal clearance. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- anastrozole
anastrozole will increase the level or effect of tacrolimus by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- armodafinil
tacrolimus will increase the level or effect of armodafinil by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- budesonide
budesonide, tacrolimus. Either increases levels of the other by decreasing metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- caspofungin
caspofungin decreases levels of tacrolimus by unspecified interaction mechanism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- chloroquine
chloroquine increases levels of tacrolimus by decreasing metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- chlorpropamide
chlorpropamide increases levels of tacrolimus by unknown mechanism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- clonidine
clonidine increases levels of tacrolimus by unknown mechanism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- clotrimazole
clotrimazole increases levels of tacrolimus by decreasing metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- cortisone
cortisone, tacrolimus. Either increases levels of the other by decreasing metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- cyclophosphamide
cyclophosphamide will increase the level or effect of tacrolimus by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- danazol
danazol increases effects of tacrolimus by decreasing metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- deflazacort
deflazacort, tacrolimus. Either increases levels of the other by decreasing metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- dexamethasone
dexamethasone, tacrolimus. Either increases levels of the other by decreasing metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- drospirenone
drospirenone will increase the level or effect of tacrolimus by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- entecavir
tacrolimus, entecavir. Either increases effects of the other by decreasing renal clearance. Minor/Significance Unknown. Coadministration with drugs that reduce renal function or compete for active tubular secretion may increase serum concentrations of either entecavir or the coadministered drug.
- fexofenadine
tacrolimus will increase the level or effect of fexofenadine by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- fludrocortisone
fludrocortisone, tacrolimus. Either increases levels of the other by decreasing metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- fluoxymesterone
fluoxymesterone increases effects of tacrolimus by decreasing metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- food
food decreases levels of tacrolimus by inhibition of GI absorption. Applies only to oral form of both agents. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- glimepiride
glimepiride increases levels of tacrolimus by unknown mechanism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- glipizide
glipizide increases levels of tacrolimus by unknown mechanism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- glyburide
glyburide increases levels of tacrolimus by unknown mechanism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- hydrocortisone
hydrocortisone, tacrolimus. Either increases levels of the other by decreasing metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- loratadine
tacrolimus will increase the level or effect of loratadine by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- mesterolone
mesterolone increases effects of tacrolimus by decreasing metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- methylprednisolone
methylprednisolone, tacrolimus. Either increases levels of the other by decreasing metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- oxandrolone
oxandrolone increases effects of tacrolimus by decreasing metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- oxymetholone
oxymetholone increases effects of tacrolimus by decreasing metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- prednisolone
prednisolone, tacrolimus. Either increases levels of the other by decreasing metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- prednisone
prednisone, tacrolimus. Either increases levels of the other by decreasing metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- pyrazinamide
pyrazinamide decreases levels of tacrolimus by unknown mechanism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- testosterone
testosterone increases effects of tacrolimus by decreasing metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- testosterone buccal system
testosterone buccal system increases effects of tacrolimus by decreasing metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- testosterone topical
testosterone topical increases effects of tacrolimus by decreasing metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- tolazamide
tolazamide increases levels of tacrolimus by unknown mechanism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- tolbutamide
tolbutamide increases levels of tacrolimus by unknown mechanism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- triamcinolone acetonide injectable suspension
triamcinolone acetonide injectable suspension, tacrolimus. Either increases levels of the other by decreasing metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
Adverse Effects
>10% (Prograf)
Tremor (54%)
Hypertension (50%)
Hypophosphatemia (49%)
Increased creatinine (45%)
Infection (45%)
Headache (44%)
Diarrhea (44%)
Nausea (38%)
Peripheral edema (36%)
Constipation (35%)
Urinary tract infection (34%)
Hypomagnesemia (34%)
Asthenia (34%)
Abdominal pain (33%)
Pain (32%)
Insomnia (32%)
Hyperlipemia (31%)
Hyperkalemia (31%)
Anemia (30%)
Vomiting (29%)
Dyspepsia (28%)
Fever (29%)
Arthralgia (25%)
Back pain (24%)
Diabetes mellitus (24%)
Paresthesia (23%)
Hypokalemia (22%)
Hyperglycemia (22%)
Dyspnea (22%)
Dizziness (19%)
Chest Pain (19%)
Increased cough (18%)
Edema (18%)
Skin rash (17%)
Pruritus (15%)
Leukopenia (15%)
>10% (Envarsus XR)
All infections (46%)
Respiratory infections (26%)
Diarrhea (14%)
Increased creatinine (12%)
>10% (Astagraf XL)
All infections (69%)
Diarrhea (45%)
Constipation (40%)
Nausea (36%)
Peripheral edema (36%)
Tremor (35%)
Respiratory infections (34%)
Anemia (33%)
Hypertension (28%)
Vomiting (25%)
Hypomagnesemia (24%)
Insomnia (24%)
Hypophosphatemia (23%)
Serious infections (22%)
Headache (22%)
Hyperkalemia (20%)
Increased blood creatinine (19%)
Urinary tract infections (16%)
Fatigue (16%)
Leukopenia (16%)
Hyperlipidemia (16%)
Hyperglycemia (16%)
1-10% (Astagraf XL)
Cytomegalovirus infection (10%)
Bacterial infections (8%)
Gastroenteritis (7%)
Polyomavirus infections (3%)
1-10% (Envarsus XR)
Urinary tract infections (9-10%)
Nasopharyngitis (9%)
Headache (9%)
Serious infections (8%)
Bacterial infections (7%)
Upper respiratory tract infection (7%)
Peripheral edema (7%)
Hypertension (4%)
Fungal infections (4%)
Gastrointestinal infections (2%)
Cytomegalovirus infections (2%)
BK virus (2%)
Postmarketing Reports
Blood and lymphatic system disorders: Agranulocytosis, disseminated intravascular coagulation, hemolytic uremic syndrome, febrile neutropenia, pancytopenia, pure red cell aplasia, coagulopathy, thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura, prolonged activated partial thromboplastin time, decreased blood fibrinogen
Cardiac disorders: Cardiac arrest, myocardial infarction, ventricular fibrillation, congestive cardiac failure, hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, pericardial effusion, angina pectoris, supraventricular extrasystoles, supraventricular tachycardia, bradycardia, Torsade de Pointes, QT prolongation
Ear disorders: Hearing loss
Eye disorders: Blindness, optic neuropathy, optic atrophy, photophobia
Gastrointestinal disorders: Gastrointestinal hemorrhage, gastrointestinal perforation, pancreatitis, peritonitis, stomach ulcer, intestinal obstruction, ascites, colitis, ileus, impaired gastric emptying, dysphagia
Hepatobiliary disorders: Hepatic failure, hepatic necrosis, cirrhosis, cholangitis, venoocclusive liver disease, bile duct stenosis, hepatic steatosis, jaundice. acute and chronic hepatitis
Hypersensitivity reactions: Hypersensitivity, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, toxic epidermal necrolysis, urticaria
Immune system disorders: Graft versus host disease (acute and chronic)
Investigations: Increased international normalized ratio
Metabolism and nutrition disorders: Hypoproteinemia
Musculoskeletal and connective tissue disorders: Rhabdomyolysis, myalgia, polyarthritis, pain in extremity including Calcineurin-Inhibitor Induced Pain Syndrome (CIPS)
Neoplasms: Lymphoma including EBV-associated lymphoproliferative disorder, hepatosplenic T-cell lymphoma, PTLD, leukemia, melanoma
Nervous system disorders: Cerebral infarction, progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy (PML) sometimes fatal, posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome (PRES), coma, status epilepticus, quadriplegia, flaccid paralysis, hemiparesis, aphasia, syncope, carpal tunnel syndrome, nerve compression, mutism, dysarthria, somnolence
Psychiatric disorders: Mental status changes
Renal and urinary disorders: Hemorrhagic cystitis, hematuria, urinary retention, urinary incontinence
Respiratory, thoracic and mediastinal disorders: Interstitial lung disease, pulmonary hypertension, lung infiltration, rhinitis allergic, hiccups
Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders: Hyperpigmentation, photosensitivity
Vascular disorders: Hemorrhage, thrombotic microangiopathy
Warnings
Black Box Warnings
Serious infections and malignancies
- Increased risk for developing serious infections and malignancies, including lymphoma and skin malignancies, with tacrolimus or other immunosuppressants that may lead to hospitalization or death
Increased mortality in female liver transplant patients
- Astagraf XL
- Increased mortality in female transplant recipients was observed in clinical trial of liver transplantation; use of extended release formulation in liver transplantation is not recommended
Experienced physician
- Only healthcare providers experienced in immunosuppressive therapy and management of organ transplant patients should prescribe the drug; patients therapy should be managed in facilities equipped and staffed with laboratory and supportive medical resources; healthcare provider responsible for maintenance therapy should have complete information required for follow up of patient
Contraindications
Hypersensitivity to tacrolimus or any component of the formulation, including castor oil (Prograf)
Cautions
Hypersensitivity reactions, including anaphylaxis reported with injection formulation, which contains polyoxyl 60 hydrogenated castor oil (HCO-60), a castor oil derivative; limit IV use to patients unable to take orally; monitor patient for 30 min after initiation of infusion and then at frequent intervals; discontinue infusion if anaphylaxis occurs; transition patient from IV to oral dosing as soon as patient can tolerate oral administration
Increased risk of infections and lymphoma, including latent virus activation (eg, BK virus-induced nephropathy)
Patients receiving immunosuppressants are at increased risk of developing bacterial, viral, fungal, and protozoal infections, including opportunistic infections; these infections may lead to serious, including fatal, outcomes; serious viral infections reported include, cytomegalovirus infections; CMV seronegative transplant patients who receive an organ from a CMV seropositive donor are at higher risk of developing CMV viremia and CMV disease; monitor for the development of infection and adjust the immunosuppressive regimen to balance the risk of rejection with the risk of infection (see Black Box Warnings)
Medication errors (eg, substitution and dispensing errors, between tacrolimus immediate-release products and tacrolimus extended-release products) reported outside the U.S; which led to serious adverse reactions such as graft rejection, or other adverse reactions due to under-or over-exposure to tacrolimus; not interchangeable or substitutable for tacrolimus extended-release tablets, tacrolimus immediate-release capsules or tacrolimus for oral suspension; changes between tacrolimus immediate-release and extended-release dosage forms must occur under physician supervision
Hypertension may occur; may treat with antihypertensives that are non-potassium-sparing diuretics; concurrent use of calcium channel blockers may require tacrolimus dosage adjustment
Mild-to-severe hyperkalemia may occur; avoid use of potassium sparing diuretics
Myocardial hypertrophy reported (reversible with dose reduction or discontinuation)
QT prolongation reported; consider obtaining electrocardiograms and monitoring electrolytes periodically during treatment in patients with congestive heart failure, bradyarrhythmias, patients taking antiarrhythmic medications or other medicinal products that lead to QT prolongation, and those with electrolyte disturbances, including hypokalemia, hypomagnesemia, or hypocalcemia
Cases of pure red-cell aplasia reported; if this is diagnosed, consider discontinuing tacrolimus
Gastrointestinal perforation; all reported cases were considered a complication of transplant surgery or accompanied by infection, diverticulum, or malignant neoplasm
Increased risk of malignancy is related to intensity/duration of therapy; limit or avoid sun and ultraviolet light exposure; use appropriate sun protection; post-transplant lymphoproliferative disorder related to EBV infection reported in immunosuppressed organ transplant patients; risk highest in young children
African-Americans may need to be titrated to higher dosages to achieve the target tacrolimus concentrations
Graft rejection and other serious adverse effects have resulted from medication errors with extended release dosage form; patients and caregivers are advised to recognize appearance extended release tablets
Monitor blood glucose; new onset of diabetes after transplants reported
Can cause acute or chronic nephrotoxicity in transplant patients due to vasoconstrictive effect on renal vasculature, toxic tubulopathy and tubular-interstitial effects; acute renal impairment associated with tacrolimus toxicity can result in high serum creatinine, hyperkalemia, decreased secretion of urea and hyperuricemia; usually reversible; monitor renal function; consider dosage reduction
Neurotoxicity including risk of posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome (PRES) reported; monitor for neurologic abnormalities; reduce dosage or discontinue
Thrombotic microangiopathy
- Cases of thrombotic microangiopathy (TMA), including hemolytic uremic syndrome (HUS) and thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura (TTP), reported may have a multifactorial etiology
- Risk factors for TMA that can occur in transplant patients include, for example, severe infections, graft-versus-host disease (GVHD), human leukocyte antigen (HLA) mismatch, use of calcineurin inhibitors and mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) inhibitors; these risk factors may, either alone or combined, contribute to risk of TMA.
- In patients with signs and symptoms of TMA, consider tacrolimus as a risk factor. Concurrent use of tacrolimus and mTOR inhibitors may contribute to the risk of TMA
Posttransplant diabetes mellitus
- Risk of posttransplant diabetes mellitus, especially in black and Hispanic patients; may occur in patients without pretransplant history of diabetes mellitus
- Insulin dependence may be reversible
- Black patients may require higher doses in kidney transplant
- Monitor blood glucose frequently
- Discontinue cyclosporine 24 hours before starting tacrolimus
- Combination immunosuppressant therapy
Drug interactions overview
- Use with strong CYP3A inhibitors and inducers: a rapid, sharp rise in tacrolimus levels reported after co-administration with a strong CYP3A4 inhibitor, clarithromycin, despite an initial reduction of tacrolimus dose; early and frequent monitoring of tacrolimus whole blood trough levels for occurrence of adverse reactions, including QT prolongation recommended
- Concomitant use of strong CYP3A inducers may increase metabolism of tacrolimus, leading to lower whole blood trough concentrations and greater risk of rejection
- Not for use with sirolimus; associated with an excess mortality, graft loss, and hepatic artery thrombosis (HAT); the concomitant administration of sirolimus (2 mg per day) in heart transplant patients associated with increased risk of renal function impairment, wound healing complications, and insulin-dependent post-transplant diabetes mellitus
- Use caution with concurrent administration of nephrotoxic agents, in patients with elevated serum creatinine and tacrolimus whole blood trough concentrations greater than recommended range, consider dosage reduction or temporary interruption of tacrolimus administration; risk for nephrotoxicity may increase when drug is concomitantly administered with CYP3A inhibitors (by increasing tacrolimus whole blood concentrations) or drugs associated with nephrotoxicity (eg, aminoglycosides, ganciclovir, amphotericin B, cisplatin, nucleotide reverse transcriptase inhibitors, protease inhibitors)
- When tacrolimus is used concurrently with other known nephrotoxic drugs, monitor renal function and tacrolimus blood concentrations, and adjust dose of both tacrolimus and/or concomitant medications during concurrent use
- Avoid use of live vaccines during treatment with tacrolimus
- Inactivated vaccines noted to be safe for administration after transplantation may not be sufficiently immunogenic during treatment
Pregnancy & Lactation
Pregnancy
There is a pregnancy registry that monitors pregnancy outcomes in women exposed to drug during pregnancy; the transplantation pregnancy registry international (TPRI) is a voluntary pregnancy exposure registry that monitors outcomes of pregnancy in female transplant recipients and those fathered by male transplant recipients exposed to immunosuppressants including tacrolimus; healthcare providers are encouraged to advise their patients to register by contacting the Transplantation Pregnancy Registry International at 1-877-955-6877 or https://www.transplantpregnancyregistry.org/
Tacrolimus can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman; data from postmarketing surveillance and TPRI suggest that infants exposed to tacrolimus in utero are at a risk of prematurity, birth defects/congenital anomalies, low birth weight, and fetal distress; advise pregnant women of potential risk to fetus; administration of oral tacrolimus to pregnant rabbits and rats throughout the period of organogenesis was associated with maternal toxicity/lethality, and an increased incidence of abortion, malformation and embryofetal death at clinically relevant doses (0.5 to 6.9 times the recommended clinical dose range [0.2 to 0.075 mg/kg/day], on a mg/m2 basis)
Risks during pregnancy are increased in organ transplant recipients; the risk of premature delivery following transplantation is increased; pre-existing hypertension and diabetes confer additional risk to the pregnancy of an organ transplant recipient; pre-gestational and gestational diabetes are associated with birth defects/congenital anomalies, hypertension, low birth weight and fetal death; cholestasis of pregnancy (COP) was reported in 7% of liver or liver-kidney (LK) transplant recipients, compared with approximately 1% of pregnancies in the general population; however, COP symptoms resolved postpartum and no long term effect on offsprings was reported
Tacrolimus may increase hyperglycemia in pregnant women with diabetes (including gestational diabetes); monitor maternal blood glucose levels regularly
Therapy may exacerbate hypertension in pregnant women and increase pre-eclampsia; monitor and control blood pressure
Renal dysfunction, transient neonatal hyperkalemia and low birth weight have been reported at time of delivery in infants of mothers taking drug
There is an increased risk for premature delivery (< 37 weeks) following transplantation and maternal exposure to drug.
Contraception
- Therapy can cause fetal harm when administered to pregnant women; advise female and male patients of reproductive potential to speak to their healthcare provider on family planning options including appropriate contraception prior to starting treatment
Infertility
- Based on findings in animals, male and female fertility may be compromised by treatment
Lactation
Controlled lactation studies have not been conducted in humans; however tacrolimus has been reported to be present in human milk; effects of tacrolimus on breastfed infant, or on milk production have not been assessed
Tacrolimus is excreted in rat milk and in peri-/postnatal rat studies, exposure to tacrolimus during postnatal period was associated with developmental toxicity in offspring at clinically relevant doses
The developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with mother’s clinical need for drug and any potential adverse effects on breastfed child from drug or from underlying maternal condition
Pregnancy Categories
A: Generally acceptable. Controlled studies in pregnant women show no evidence of fetal risk.
B: May be acceptable. Either animal studies show no risk but human studies not available or animal studies showed minor risks and human studies done and showed no risk. C: Use with caution if benefits outweigh risks. Animal studies show risk and human studies not available or neither animal nor human studies done. D: Use in LIFE-THREATENING emergencies when no safer drug available. Positive evidence of human fetal risk. X: Do not use in pregnancy. Risks involved outweigh potential benefits. Safer alternatives exist. NA: Information not available.Pharmacology
Mechanism of Action
Calcineurin inhibitor; inhibits T-cell activation and proliferation, humoral immunity
Macrolide antibiotic; potent immunosuppressant
Absorption
Bioavailability: 7-55% (children); 7-32% (adults)
Peak plasma time: 0.5-6 hr
Distribution
Protein bound: 99%
Vd: 0.5-4.7 L/kg (children); 0.55-2.47 L/kg (adults)
Metabolism
Metabolized in liver by CYP3A4
Metabolites: 13-O-demethyl tacrolimus (major)
P-gp substrate
Elimination
Half-life: 23-46 hr (immediate release); 34.5-41 hr (extended release)
Excretion: Feces (94%); urine (<1%)
Administration
IV Incompatibilities
Y-site: Acyclovir, ganciclovir
IV Compatibilities
Solution: D5W, NS
Additive: Cimetidine
Y-site (partial list): Ampicillin, ampicillin-sulbactam, calcium gluconate, cefazolin, ciprofloxacin, dopamine, fluconazole, furosemide, heparin, lorazepam, metoclopramide, metronidazole, morphine sulfate, multivitamins, penicillin G potassium, potassium chloride, propranolol, sodium bicarbonate, trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole, vancomycin
IV Preparation
Dilute with NS or D5W to 0.004-0.02 mg/mL
Do not store diluted solutions in a polyvinyl chloride (PVC) container due to decreased stability and the potential for extraction of phthalates from PVC containers
Visually inspect product for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration, whenever solution and container permit
Due to the chemical instability of tacrolimus in alkaline media, mix or co-infuse with solutions of pH ≥9
IV Administration
Administer by IV continuous infusion only (use infusion pump)
In situations where more dilute solutions are utilized (eg, pediatric dosing.), utilize PVC-free tubing to minimize the potential for significant drug adsorption onto the tubing
Oral Suspension Preparation
Can cause fetal harm; follow applicable special handling and disposal procedures
Calculate required dose; use the minimum whole number of packets that corresponds to the required morning or evening dose
If morning or evening dose is not covered by the whole number of packets, use one additional 0.2 mg packet to round up the dose
Do not use tubing, syringes and other equipment (cups) containing PVC to prepare or administer tacrolimus suspension; do not sprinkle on food
Empty the entire contents of each packet into a glass cup; ensure packet is completely empty and add 1-2 tablespoons (15-30 mL) of room temperature drinking water to cup containing the granules
Mix and administer the entire contents of the cup; granules will not completely dissolve; give immediately after preparation
Pediatric patients
- Draw up and dispense suspension via a non-PVC oral syringe
- Rinse cup or syringe with the same quantity of water (15-30 mL) and ensure all of the medication is taken
Oral Administration
Administer the same time each day, 12 hr apart
Do not eat too much grapefruit while taking tacrolimus
Capsules and granules
- Administer consistently with or without food
- Do not open capsules
Extended-release capsules or tablets
- Take preferably on an empty stomach
- Swallow whole; do not chew, divide, or crush
Missed doses
- Once daily extended-release: Take it as soon as possible within 14 hr (Astagraf XL) or 15 hr (Envarsus XR) after missing the dose; beyond the 14-hr or 15-hr time frame, wait until the usual scheduled time to take the next regular daily dose; do not double the next dose
Storage
Envarsus XR: Store at 25°C (68-77°F); excursions permitted to 15-30°C (59-86°F)
Astagraf XL: Store at 25°C (68-77°F); excursions permitted to 15-30°C (59-86°F)
Prograf
- Capsules: Store at 20-25°C (68-77°F); excursions permitted to 15-30°C (59-86°F)
-
Granules
- Unit dose packets: Store at 20-25°C (68-77°F); excursions permitted to 15-30°C (59-86°F)
-
Injection
- Unused vials: Store at 5-25°C (41-77°F)
- Diluted solutions: Discard after 24 hr
Images
| BRAND | FORM. | UNIT PRICE | PILL IMAGE |
|---|---|---|---|
| tacrolimus topical - | 0.1 % ointment |  | |
| tacrolimus topical - | 0.1 % ointment |  | |
| tacrolimus topical - | 0.1 % ointment |  | |
| tacrolimus topical - | 0.03 % ointment |  | |
| tacrolimus topical - | 0.03 % ointment |  | |
| tacrolimus topical - | 0.03 % ointment |  | |
| tacrolimus topical - | 0.03 % ointment |  | |
| tacrolimus topical - | 0.1 % ointment |  | |
| tacrolimus topical - | 0.03 % ointment |  | |
| tacrolimus topical - | 0.03 % ointment |  | |
| tacrolimus topical - | 0.1 % ointment |  | |
| tacrolimus topical - | 0.1 % ointment |  | |
| tacrolimus topical - | 0.03 % ointment |  | |
| tacrolimus topical - | 0.1 % ointment |  | |
| tacrolimus topical - | 0.1 % ointment |  | |
| tacrolimus topical - | 0.1 % ointment |  | |
| tacrolimus topical - | 0.1 % ointment |  | |
| tacrolimus topical - | 0.03 % ointment |  | |
| tacrolimus topical - | 0.03 % ointment |  | |
| tacrolimus topical - | 0.1 % ointment |  | |
| tacrolimus topical - | 0.1 % ointment |  | |
| tacrolimus topical - | 0.1 % ointment |  | |
| tacrolimus topical - | 0.1 % ointment |  | |
| tacrolimus topical - | 0.1 % ointment | 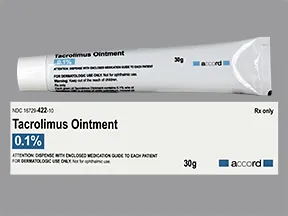 | |
| tacrolimus topical - | 0.03 % ointment | 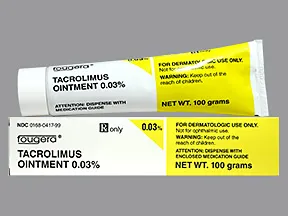 | |
| tacrolimus topical - | 0.03 % ointment | 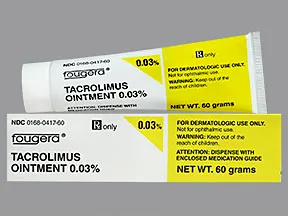 | |
| Prograf oral - | 1 mg capsule | 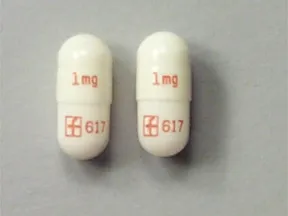 | |
| Prograf oral - | 1 mg package |  | |
| Prograf oral - | 0.2 mg package |  | |
| Prograf oral - | 5 mg capsule | 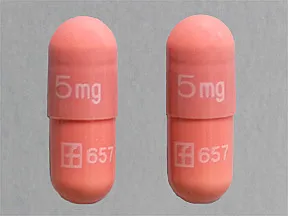 | |
| Prograf oral - | 0.5 mg capsule | 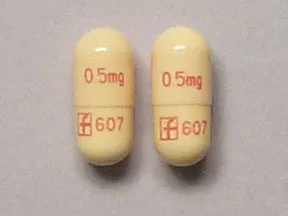 | |
| tacrolimus oral - | 1 mg capsule |  | |
| tacrolimus oral - | 1 mg capsule |  | |
| tacrolimus oral - | 0.5 mg capsule | 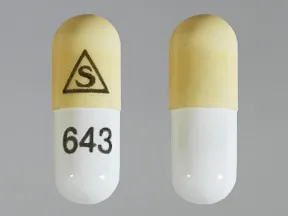 | |
| tacrolimus oral - | 0.5 mg capsule | 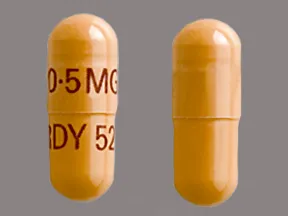 | |
| tacrolimus oral - | 1 mg capsule | 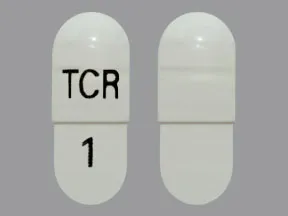 | |
| tacrolimus oral - | 1 mg capsule | 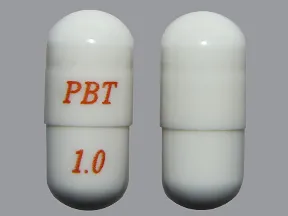 | |
| tacrolimus oral - | 5 mg capsule |  | |
| tacrolimus oral - | 5 mg capsule | 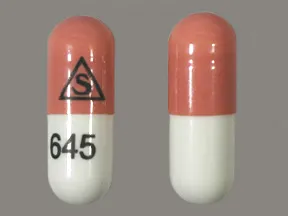 | |
| tacrolimus oral - | 0.5 mg capsule |  | |
| tacrolimus oral - | 5 mg capsule |  | |
| tacrolimus oral - | 1 mg capsule |  | |
| tacrolimus oral - | 1 mg capsule |  | |
| tacrolimus oral - | 5 mg capsule |  | |
| tacrolimus oral - | 5 mg capsule |  | |
| tacrolimus oral - | 0.5 mg capsule |  | |
| tacrolimus oral - | 1 mg capsule |  | |
| tacrolimus oral - | 0.5 mg capsule |  | |
| tacrolimus oral - | 1 mg capsule |  | |
| tacrolimus oral - | 0.5 mg capsule |  | |
| tacrolimus oral - | 5 mg capsule |  | |
| tacrolimus oral - | 0.5 mg capsule | 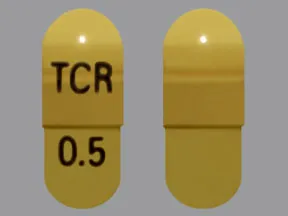 | |
| Prograf intravenous - | 5 mg/mL solution | 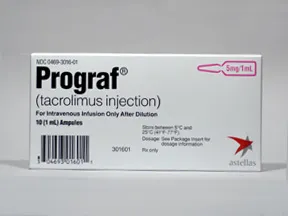 | |
| Astagraf XL oral - | 5 mg capsule |  | |
| Astagraf XL oral - | 0.5 mg capsule |  | |
| Astagraf XL oral - | 1 mg capsule |  | |
| Envarsus XR oral - | 0.75 mg tablet |  | |
| Envarsus XR oral - | 4 mg tablet |  | |
| Envarsus XR oral - | 1 mg tablet |  |
Copyright © 2010 First DataBank, Inc.
Patient Handout
tacrolimus topical
TACROLIMUS - TOPICAL
(ta-KROE-li-mus)
COMMON BRAND NAME(S): Protopic
WARNING: Patients have benefited from tacrolimus when it is used correctly. Long-term safety for this drug is not known at this time. There have been rare reports of cancers (such as skin cancer, lymphoma) in patients using tacrolimus. It is not known whether tacrolimus caused these cancers when used on the skin. Further studies to determine the long-term safety of this product are ongoing. In the unlikely event that unusual lumps, swollen glands, or growths (especially on the skin) occur, contact your doctor right away.The US Food and Drug Administration recommends the following: This drug should be used only if other drugs have failed or if other medications are not considered appropriate by your doctor. Tacrolimus should be used on the skin for short treatment periods only. If needed, treatment may be repeated with breaks in between. Use the smallest amount that will treat your condition properly, and apply only on the affected skin. Also, this medication should not be used by children younger than 2 years. As with all medications, discuss the risks, benefits, and proper use of this medication with your doctor.
USES: This form of tacrolimus is used on the skin to treat a skin condition called eczema (atopic dermatitis) in patients who have not responded well to (or should not use) other eczema medications.Eczema is an allergic-type condition that causes red, irritated, and itchy skin. This drug works by weakening the skin's defense (immune) system, thereby decreasing the allergic reaction and relieving the eczema. Tacrolimus belongs to a class of drugs known as topical calcineurin inhibitors (TCIs).For children 2 to 15 years of age, the lower strength product should be used.This medication is not recommended if you have a history of a certain rare genetic disorder (Netherton's syndrome). Also, this medication should not be used by anyone who has a weakened immune system (for example, following an organ transplant).
HOW TO USE: Read the Medication Guide provided by your pharmacist before you start using tacrolimus and each time you get a refill. If you have any questions, consult your doctor or pharmacist.Wash your hands with soap and water before using this medication. Apply a thin layer to the affected areas of skin as directed by your doctor, usually twice daily. Rub the medication into the skin gently and completely. Wash your hands after using this product unless your hands are being treated. If your doctor recommends a moisturizer, apply it after this medication.This product is for use on the skin only. Avoid getting this medication in your eyes or on the inside of your nose or mouth. If you do get the medication in those areas, flush with plenty of water. Do not apply this medication to open wounds or infected areas. Do not cover the treated area with plastic or waterproof bandages unless directed to do so by your doctor. Do not bathe, shower, or swim right after applying this medication. This could wash it off the treated area.Use this medication exactly as directed. Your doctor may instruct you to stop using it once your eczema has cleared and to start using it again if symptoms reappear. Consult your doctor for details.Inform your doctor if your condition does not improve after 6 weeks of using this medication or if your condition worsens at any time.
SIDE EFFECTS: Stinging, burning, soreness, or itching in the area of treated skin may occur during the first few days of treatment. Headache, acne, small red bumps on the skin (folliculitis), stomach upset, flu-like symptoms (such as fever, chills, runny nose, sore throat, muscle aches), or increased sensitivity of the skin to hot/cold/pain/touch may also occur. If any of these effects last or get worse, tell your doctor or pharmacist promptly.Remember that this medication has been prescribed because your doctor has judged that the benefit to you is greater than the risk of side effects. Many people using this medication do not have serious side effects.Tell your doctor right away if you have any serious side effects, including: unusual tiredness, back/joint/muscle pain, appearance of any skin infections or sores (such as chicken pox, shingles, lip sores, tumors, warts), chest pain.A very serious allergic reaction to this drug is rare. However, get medical help right away if you notice any symptoms of a serious allergic reaction, including: rash, itching/swelling (especially of the face/tongue/throat), severe dizziness, trouble breathing.This is not a complete list of possible side effects. If you notice other effects not listed above, contact your doctor or pharmacist.In the US -Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or at www.fda.gov/medwatch.In Canada - Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to Health Canada at 1-866-234-2345.
PRECAUTIONS: Before using tacrolimus, tell your doctor or pharmacist if you are allergic to it; or to other macrolide medications (such as sirolimus); or if you have any other allergies. This product may contain inactive ingredients, which can cause allergic reactions or other problems. Talk to your pharmacist for more details.Before using this medication, tell your doctor or pharmacist your medical history, especially of: swollen lymph nodes (for example, due to lymphadenopathy, mononucleosis), use of light therapy (such as UVA or UVB), skin or other cancers, skin infections (such as herpes, shingles), other skin conditions, kidney disease.This drug may make you more sensitive to the effects of alcohol. Your face or skin may flush red and feel hot. Limit alcoholic beverages.This medication may make you more sensitive to the sun. Limit your time in the sun. Avoid tanning booths and sunlamps. Use sunscreen and wear protective clothing when outdoors. Tell your doctor right away if you get sunburned or have skin blisters/redness.During pregnancy, this medication should be used only when clearly needed. Discuss the risks and benefits with your doctor.It is unknown if this medication passes into breast milk. Consult your doctor before breastfeeding.
DRUG INTERACTIONS: Drug interactions may change how your medications work or increase your risk for serious side effects. This document does not contain all possible drug interactions. Keep a list of all the products you use (including prescription/nonprescription drugs and herbal products) and share it with your doctor and pharmacist. Do not start, stop, or change the dosage of any medicines without your doctor's approval.
OVERDOSE: This medicine may be harmful if swallowed. If someone has overdosed and has serious symptoms such as passing out or trouble breathing, call 911. Otherwise, call a poison control center right away. US residents can call their local poison control center at 1-800-222-1222. Canada residents can call a provincial poison control center.
NOTES: Do not share this medication with others. This drug should be used as directed for treating your current condition only. Do not use it later for another condition unless told to do so by your doctor. A different medication may be necessary in that case.Talk with your doctor about other ways to manage your eczema, such as using moisturizers and taking shorter baths/showers.
MISSED DOSE: If you miss a dose, use it as soon as you remember. If it is near the time of the next dose, skip the missed dose. Use your next dose at the regular time. Do not double the dose to catch up.
STORAGE: Store at room temperature. Keep all medications away from children and pets.Do not flush medications down the toilet or pour them into a drain unless instructed to do so. Properly discard this product when it is expired or no longer needed. Consult your pharmacist or local waste disposal company.
Information last revised March 2024. Copyright(c) 2024 First Databank, Inc.
IMPORTANT: HOW TO USE THIS INFORMATION: This is a summary and does NOT have all possible information about this product. This information does not assure that this product is safe, effective, or appropriate for you. This information is not individual medical advice and does not substitute for the advice of your health care professional. Always ask your health care professional for complete information about this product and your specific health needs.
Formulary
Adding plans allows you to compare formulary status to other drugs in the same class.
To view formulary information first create a list of plans. Your list will be saved and can be edited at any time.
Adding plans allows you to:
- View the formulary and any restrictions for each plan.
- Manage and view all your plans together – even plans in different states.
- Compare formulary status to other drugs in the same class.
- Access your plan list on any device – mobile or desktop.




